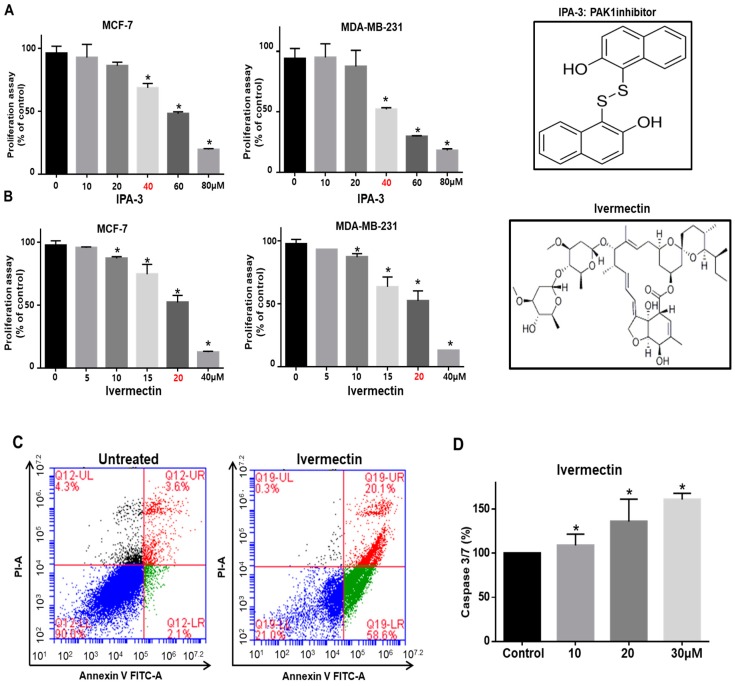
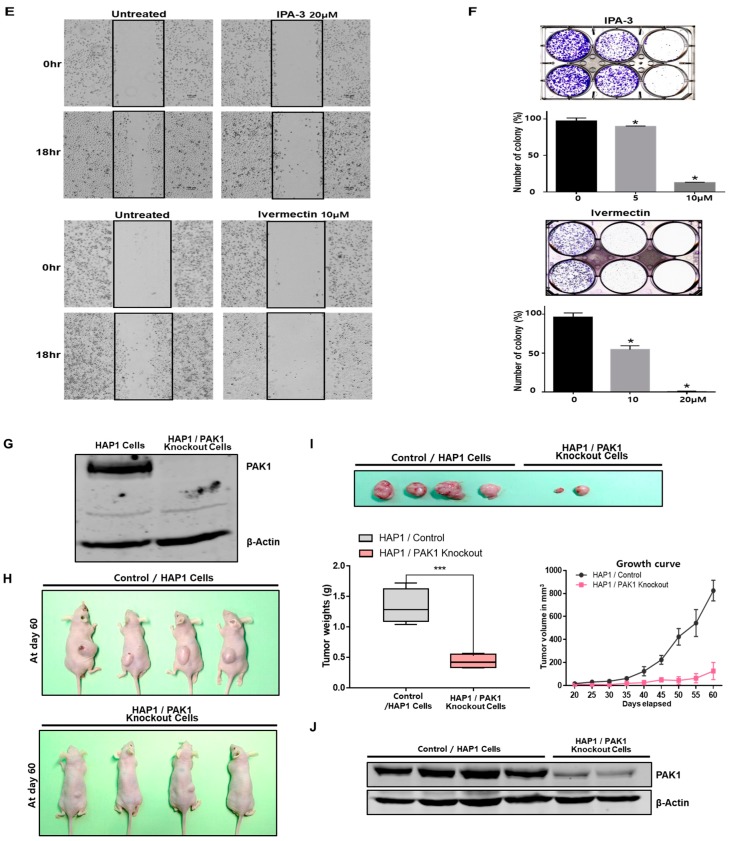
Figure 2.
PAK1 inhibition blocks breast cancer hallmark processes. (A,B) Chemical structure of IPA-3 and ivermectin, and the effect of IPA-3 and ivermectin on the proliferation of breast cancer cells. Cancer cells were incubated with IPA-3 and ivermectin for 24 h. The antiproliferation effect of IPA-3 and ivermectin was determined by using an MTS (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium) assay. (C) Ivermectin induced apoptosis in cancer cells at the indicated concentration (20 μM). Apoptotic cells were determined using Annexin V/PI staining. (D) The caspase3/7 activity of cancer cells was determined using a Caspase-Glo 3/7 assay kit (Promega). The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD); n = 3; * p < 0.05 vs. the control. (E) Effect of IPA-3 and ivermectin on cancer cell migration. The migration of cancer cells with or without IPA-3 and ivermectin was photographed at 0 and 18 h. (F) Effect of IPA-3 and ivermectin on colony formation. The one thousand dissociated cancer cells were incubated with IPA-3 and ivermectin for 1 week. Representative images were collected. The data are presented as the mean ± SD; n = 3; * p < 0.05 vs. control. (G) PAK1 expression was analyzed in wild-type and PAK1-knockout HAP1 cells by immunoblot using a PAK1-specific antibody. (H,I) Wild-type and PAK1-knockout HAP1 cell tumor growth in immunodeficient nude mice. The human PAK1-knockout HAP1 cell inhibited tumor growth. Wild-type and PAK1-knockout HAP1 cells (5 × 106 cells) were injected into nude mice subcutaneously. After seven weeks, images were captured with a camera. Tumor volumes were measured using a caliper after seven weeks. * p < 0.05 vs. control. Representative images were captured after five weeks. (J) PAK1 expression in tumors derived from wild-type and PAK1-knockout HAP1 cells was analyzed by western blot assay using a PAK1-specific antibody.