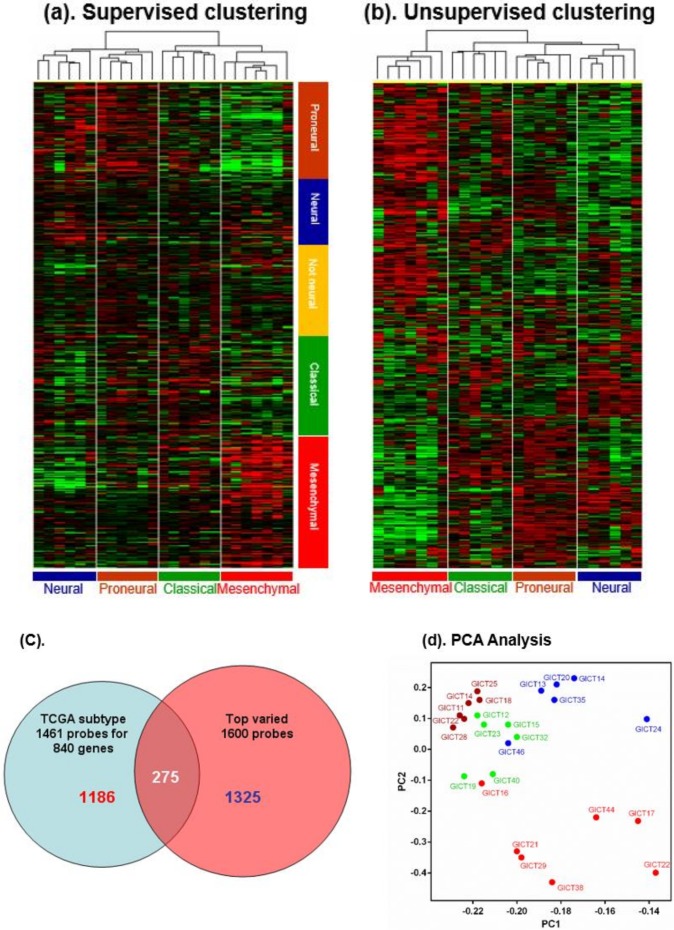
Figure 1.
(a,b): Supervised clustering (The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) 1461 probe sets) and unsupervised clustering (MTA 1600 probe sets) classified 25 glioma-initiating cell (GIC) cell lines into mesenchymal, neural, proneural, and classical subtypes. Defined GIC subtypes could be distinguished by their distinct patterns of gene expression, as related to TCGA subclass. (c) There were 275 probe sets (~20% of total) common to these two methods. (d) PCAof gene expression of the four GIC subtypes indicated that the proneural and classical GICs were most closely related and that neural and mesenchymal GICs deviated in a direction opposite to them, which supports the hypothesis that the “proneural” group has two GIC subtypes.