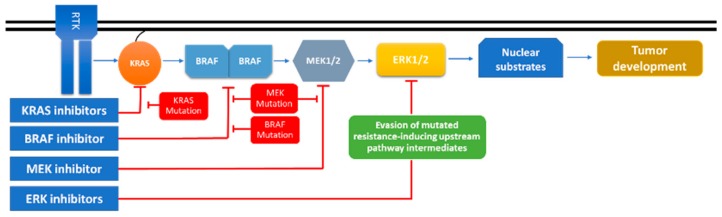
Figure 2.
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor efficiency based on mutational status—cause of resistance and weak spots. Treatment resistance is a reoccurring problem in the case of MAPK pathway inhibitors. The post-treatment acquirement or selection of tumor cells with new mutations renders the treatment useless. In the case of KRAS, BRAF, and MEK inhibitors, mutations in any of these two components can determine therapeutic resistance and relapse. Targeting ERK can become a true Achilles heel in treating cancers with MAPK signaling alterations, as ERK inhibitors target specifically downstream of the signaling cascade, with no regard of the mutational status of the upstream components (e.g., KRAS and BRAF) (KRAS: Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; BRAF: B-Raf proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase; ERK:extracellular regulated MAP kinase).