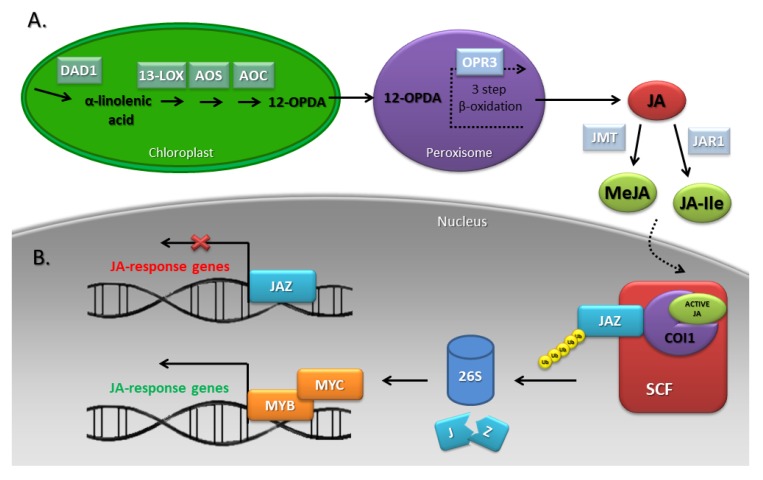
Figure 5.
JA biosynthesis (A) and signaling (B) pathways. α-linolenic acid is released from membrane phospholipid by a lipolytic enzyme phospholipase A1 DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE1 (DAD1). Next, α-linolenic acid is converted to 12-oxophytodienoic acid (12-OPDA) by 13-lipoxygenase (13-LOX), allene oxide synthase (AOS) and allene oxide cyclase (AOC). Further conversions occur in the peroxisomes, where JA is formed in a reaction catalysed by oxophytodienoic acid reductase3 (OPR3) subjected to three-step β-oxidation. Finally, in the cytosol, JA is converted to MeJA by JA carboxy methyltransferase (JMT) or JA-Ile by jasmonate amino synthetase/jasmonate resistant1 (JAR1). Bioactive JAs interact in the nucleus with the CORONATINE-INSENSITIVE1 (COI1) receptor, which leads to the activation of the SCF ubiquitin ligase E3 and the degradation of JA ZIM-domain (JAZ) repressor in 26S proteasomes. This situation allows forming the MYC-MYB complex, which regulates JA-response genes [9,76].