Figure 2.
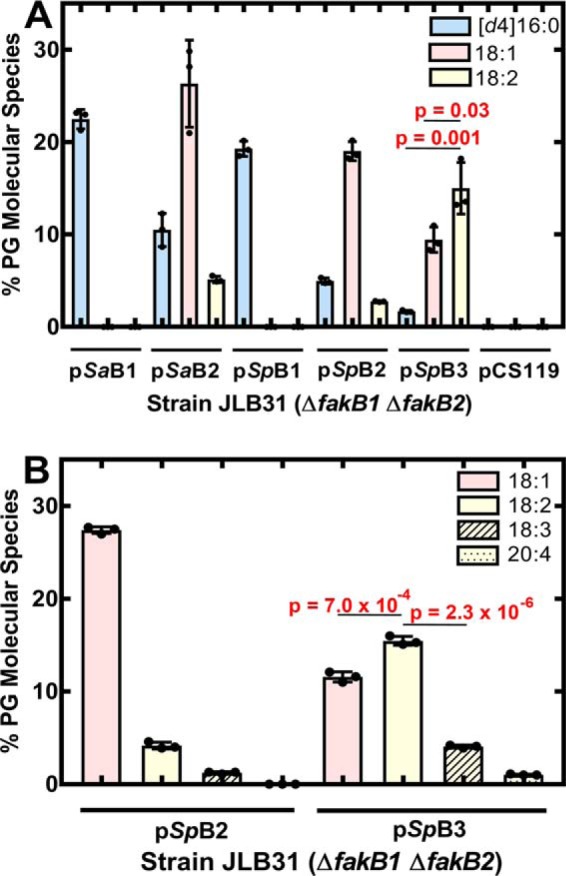
FA selectivity of S. pneumoniae FakB proteins in vivo. S. aureus strain JLB31 (ΔfakB1 ΔfakB2) contains no functional fakB genes. Plasmids derived from pCS119 (control empty vector) were constructed to drive the expression of each of the S. aureus and S. pneumoniae fakB genes using the sarA promoter and were introduced into strain JLB31. A, the strain set was labeled with an equimolar mixture of [d4]16:0, 18:1, and 18:2 (10 μm each) for 30 min and the contribution of each FA in the PG molecular species was determined by MS. B, strain JLB31 expressing SpFakB2 or SpFakB3 was labeled with an equimolar mixture of 18:1, 18:2, 18:3, and 20:4 (7.5 μm each) for 30 min, and the contribution of each unsaturated FA to the PG molecular species was determined by MS. Triplicate biological replicates were obtained, the areas under each peak in the spectra were summed and reported as a percent of the total area, and mean ± S.D. was plotted. Peaks containing elongation products, like 20:1 derived from 18:1, were included in the calculation for the contribution of the parent FA. Data are the mean ± S.D. of 3 individual data sets. Statistical differences between the FA incorporated in each strain was determined using Student's t test.
