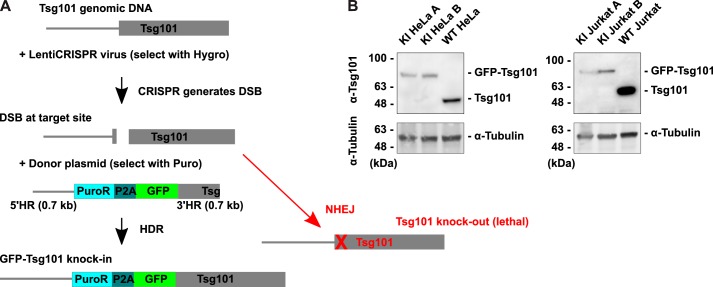
Figure 1.
GFP-Tsg101 knock-in using CRISPR-Cas9 and HDR. A, knock-in strategy. Cells were transduced with LentiCRISPRv2 to express Cas9 with sgRNA targeting the start of the Tsg101 gene and transfected with a donor template plasmid containing a puromycin resistance selection marker and a GFP tag flanked by HRs for the target site. Cas9 generates a DSB in the genomic DNA at the target site, and the donor template can be integrated into the DSB by HDR, resulting in GFP knock-in. Otherwise, the DSB is repaired by the more efficient process of NHEJ, leaving insertions or deletions that knock out Tsg101. Tsg101 knockout was lethal, which helped to select against cells that did not achieve the knock-in. B, Western blotting for Tsg101 in cell lysates of GFP-Tsg101 KI clonal lines and WT parental lines. The KI cell lines express GFP-Tsg101 at lower than WT levels and do not express untagged Tsg101. α-Tubulin is shown as a loading control.