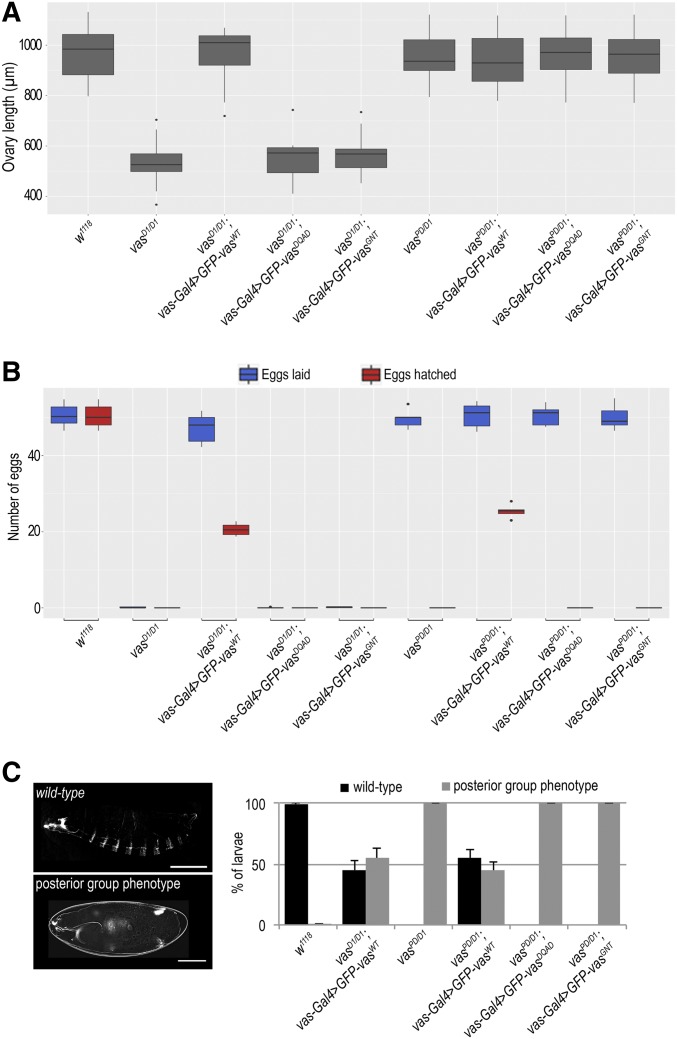
Figure 1.
Vasa helicase activity is essential for germline and embryo development. (A) Box plot representing length of ovaries of wild-type (w1118), vasD1/D1, vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasWT, vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasDQAD, vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasGNT, vasPD/D1, vasPD/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasWT, vasPD/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasDQAD, and vasPD/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasGNT flies. The measurements were performed on 10 flies (n = 10) of each genotype. Dots in the box plot represent values that are 1.5 times greater than the upper limit or 1.5 time smaller than the lower limit of the interquartile range. (B) Box plot representing the number of eggs laid and hatched from wild-type (w1118), vasD1/D1, vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasWT, vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasDQAD, vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasGNT, vasD1/D1, vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasWT, vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasDQAD, and vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasGNT flies. Five independent replicates of the experiment were performed. Dots in the box plot represent values that are 1.5 times greater than the upper limit or 1.5 time smaller than the lower limit of the interquartile range. (C) Larval cuticle phenotypes observed in wild-type (w1118), vasD1/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasWT, in vasD1/D1, vasPD/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasWT, vasPD/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasDQAD, and vasPD/D1; vas-Gal4 > GFP-VasGNT flies. Bars, 500 µm (larva) and 100 µm (unhatched larva).