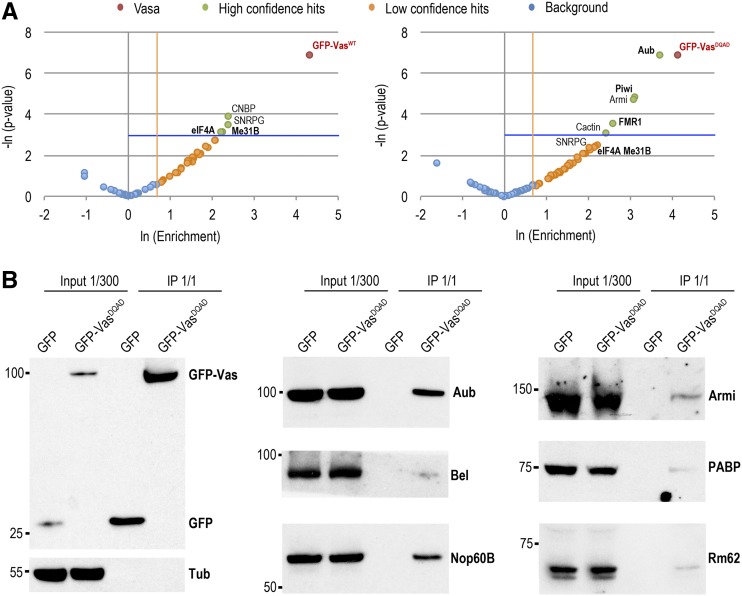
Figure 4.
Vasa associates with proteins involved in early germ cell development . (A) Mass spectrometry analysis of GFP-VasWT (left panel) and GFP-VasDQAD (right panel) co-immunoprecipitations (co-IPs). Comparison of the fold-change in abundance of proteins based on spectral count ratio (enrichment >2-fold), and statistical significance (P < 0.05) of the fold-change between GFP-Vas co-IPs and GFP negative control co-IPs. Statistically significant proteins with the highest positive fold-change were considered high-confidence hits (green); proteins with a fold-change >2 but statistically nonsignificant (P > 0.05) were considered low-confidence hits (orange); proteins below both thresholds were considered background (blue). Vasa proteins are indicated in red. Proteins previously known to interact with Vasa are in bold. Statistical analysis was performed on two biological replicates. (B) Validation of Vas-interacting proteins identified by mass spectrometry presented in A. Western blot analyses were performed using antibodies against Armi, Aub, Bel, GFP, Nop60B, PABP, Rm62, and Tub showing amounts of the proteins present in the ovarian extracts (1/300 of the input) and recovered from the anti-GFP immunoprecipitations of GFP and GFP-VasDQAD (1/1 of the immunoprecipitation).