Figure 1.
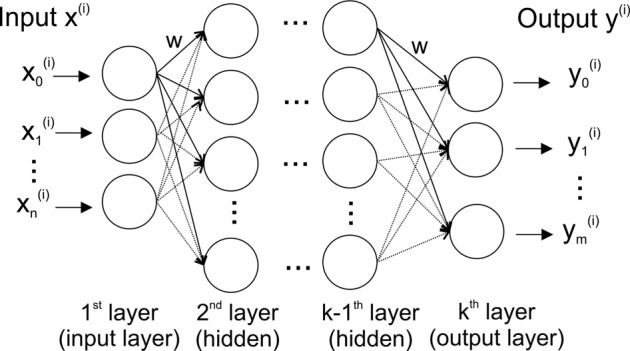
Stylized structure of a deep feedforward neural network. Each of the k layers consists of a variable number of fully connected neurons (circles). Thenetwork has as many neurons in the input layer as input variables (n), and – for classification – as many output neurons as there are classes in the data (m). A neuron is connected to all neurons in the two adjacent layers via a weighted connection (w).
