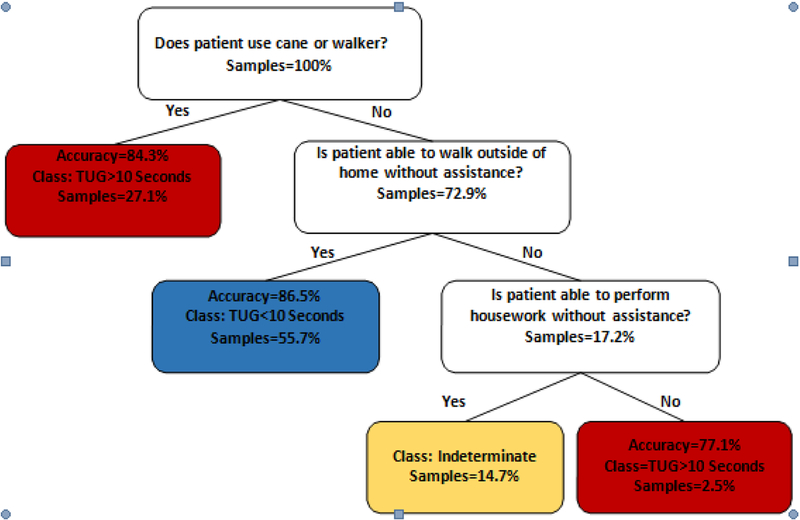
Figure 1.
The Timed Up and Go test (TUG) decision tree. Each leaf represents a classification of either TUG > ten seconds, TUG < ten seconds, or indeterminate. The accuracy of a given prediction, and samples percentage, from the original dataset which fall into each leaf are included as well. The model suggests that the get up and go frailty indicator is highly related to the fact that whether a patient uses an assistive device to walk or not. If a patient uses a cane or walker, his TUG score is > ten seconds with an accuracy of 84.3%. On the other hand, if the patient does not use a cane or walker to walk, it depends on his or her ability to walk outside the house. Then, if s/he is able to walk outside without assistance, with 86% accuracy, s/he has TUG less than ten seconds. However, if the patient’s walking outside function is impaired, and cannot do daily housework, the TUG is > ten seconds, with accuracy more than 77%.