Figure 8.
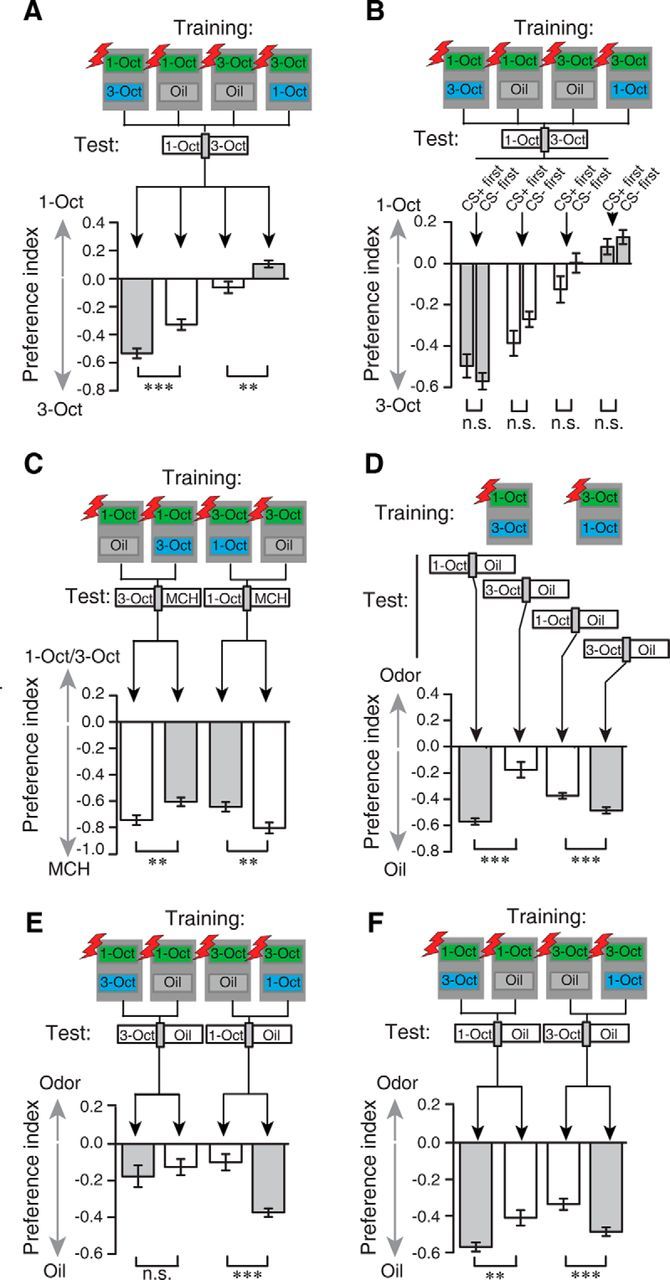
Differential training decreases generalization across similar odors as a result of conditioned inhibition. A, Comparison of absolute and differential training with 1-Oct and/or 3-Oct in a test situation for both odors. After differential training conditions (gray bars), subsequent avoidance of the odor temporally paired with the shocks (green boxes in the schematic illustration) was induced. This behavioral response was significantly lower after absolute training conditions (white bars). Note the asymmetry of the effect. ***p < 0.001 (two-sample t test). **p < 0.01 (two-sample t test). n = 16 for each experiment. Bars indicate mean ± SEM. B, The preference indices observed in A are independent from the timing of the CS+ and CS− presentation (i.e., from whether the CS+ precedes the CS− or vice versa). n.s., Not significant (p > 0.05; two-sample t test). Bars indicate mean ± SEM; n = 8 for each experiment. C, Conditioned inhibition is demonstrated by either differential (gray bars) or absolute (white bars) training and a subsequent test of the odorant not paired with electric shocks compared with a novel, dissimilar odorant MCH. The presentation of the CS− during differential training decreased the avoidance of the generalized odor. **p < 0.01 (two-sample t test). n = 16 for each experiment. Bars indicate mean ± SEM. D, Differential training of the similar odorants and subsequent presentation of the CS+ or the CS− only results in strong, generalized avoidance of the trained CS+, but weaker generalized avoidance of the CS−. E, Comparison of odor preferences after absolute (white bars) and differential training (gray bars) with 1-Oct and 3-Oct and a subsequent test for the nonreinforced odor against the diluent. Whereas the behavior was not different for 1-Oct as a CS+, pairing of 3-Oct with electric shocks resulted in a significantly stronger avoidance of 1-Oct after differential training. n.s., Not significant (p > 0.05; two-sample t test). ***p < 0.001 (two-sample t tests). n = 16 for each experiment. Bars indicate mean ± SEM. F, Comparison of absolute and differential training with 1-Oct and 3-Oct and a subsequent test for the CS+ against the diluent. Differential training (gray bars) resulted in a significantly stronger avoidance of the CS+ compared with absolute training (white bars). ***p < 0.001 (two-sample t test). **p < 0.01 (two-sample t test). n = 16 for each experiment. Bars indicate mean ± SEM.
