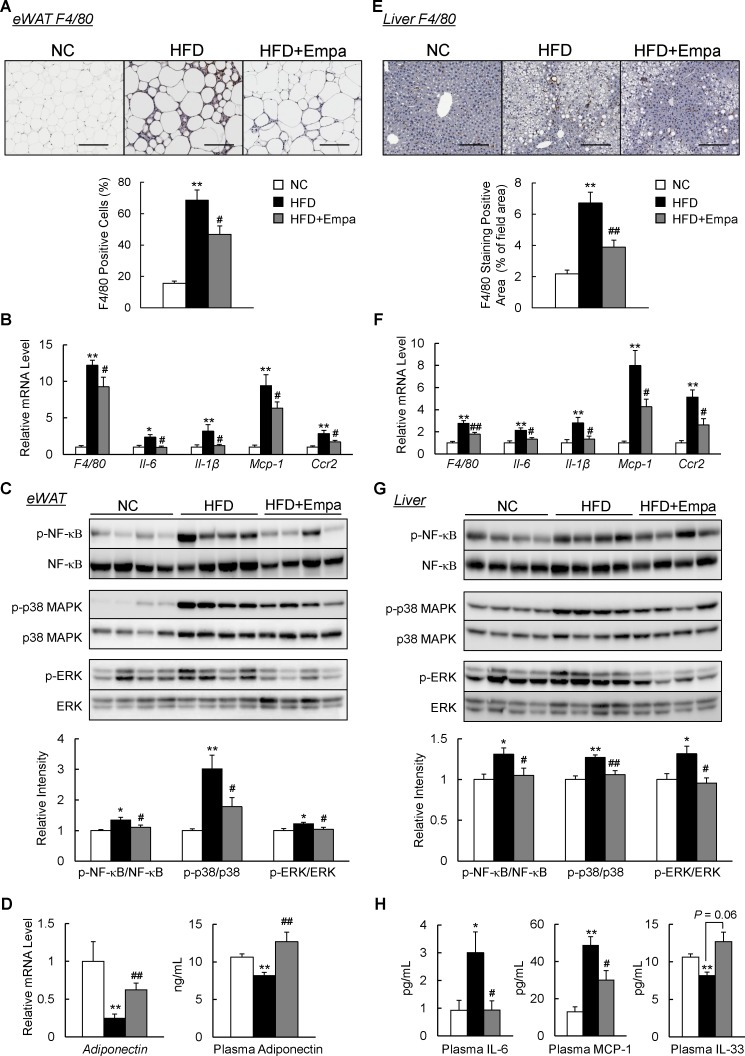
Figure 4.
Empagliflozin (Empa) attenuated adipose tissue and liver inflammation in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice. (A) F4/80 immunostaining in the epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT). Scale bars=100 µm. (B) Levels of F4/80 and inflammatory cytokines and chemokines mRNAs in the eWAT. (C) Immunoblots of phosphorylated nuclear factor-κB (p-NF-κB p65), phosphorylated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p-p38 MAPK), phosphorylated extracellular signal-related kinase (p-ERK) and their total protein contents in the eWAT. (D) Levels of adiponectin mRNAs in the eWAT and adiponectin in the plasma. (E) F4/80 immunostaining in the liver. Scale bars=100 µm. (F) Levels of F4/80 and inflammatory cytokines and chemokines mRNAs in the liver. (G) Immunoblots of p-NF-κB p65, p-p38 MAPK and p-ERK, and their total protein contents in the liver. (H) Plasma interleukin (IL)-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 and IL-33 contents. Data are presented as means±SEM, n=7–8. *P<0.05 and **p<0.01, respectively, for comparisons with normal chow (NC)-fed mice; #p<0.05 and ##p<0.01, respectively, for comparisons with HFD-fed mice.