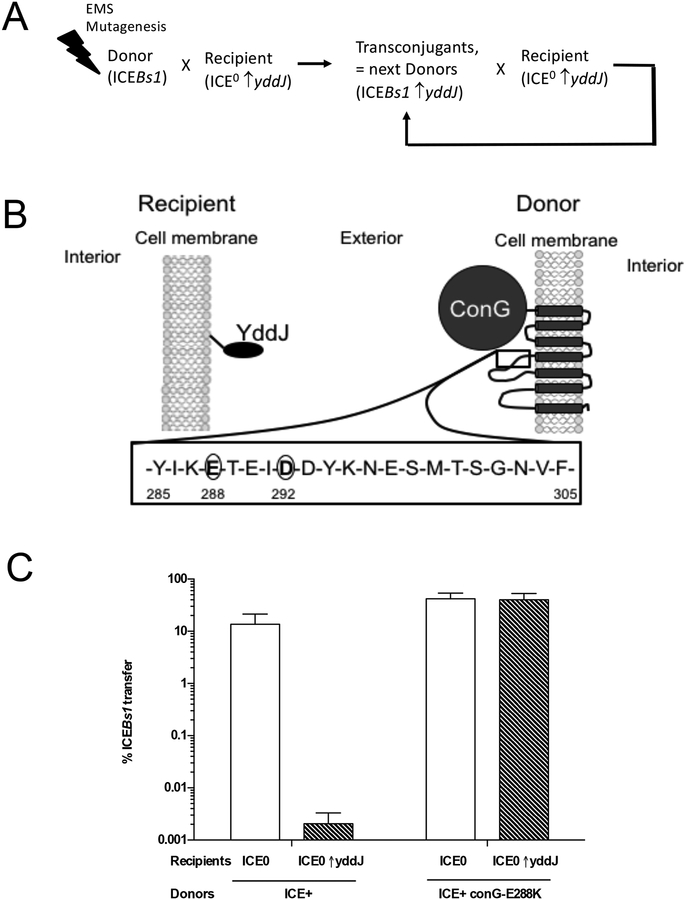
Fig. 4. Isolation of exclusion-resistant conG mutations in ICEBs1.
A. Schematic of the mutagenesis and enrichment screen for exclusion-resistant mutations in ICEBs1 (described in the text and Methods).
B. Schematic of YddJ and ConG predicted topologies. YddJ is a putative lipoprotein. Results from proteomic fractionation studies indicated that YddJ is associated with the cell membrane but that it is not a transmembrane protein (Otto et al., 2010). ConG is predicted to have seven transmembrane regions. Residues 285–305 of the extracellular loop between the third and fourth transmembrane regions are shown with the residues (288 and 292) identified in the screen for exclusion-resistance circled.
C. ICEBs1 conG-E288K donors are resistant to yddJ-mediated exclusion. Left two bars: percent transfer of ICEBs1 (MA1049; ICEBs1 Δ(rapI-phrI)342::kan, Pxyl-rapI). Right two bars: percent transfer of exclusion-resistant ICEBs1 (MA1089; ICEBs1 conG-E288K Δ(rapI-phrI)342::kan, Pxyl-rapI). White bars: recipients without ICEBs1 (CAL89). Dashed bars: recipients without ICEBs1 and overexpressing yddJ (MA982). Transfer was calculated as the percent number of transconjugants (KanR StrR cells) per number of initial donors. Data presented are averages from three independent experiments, with error bars depicting standard deviations.