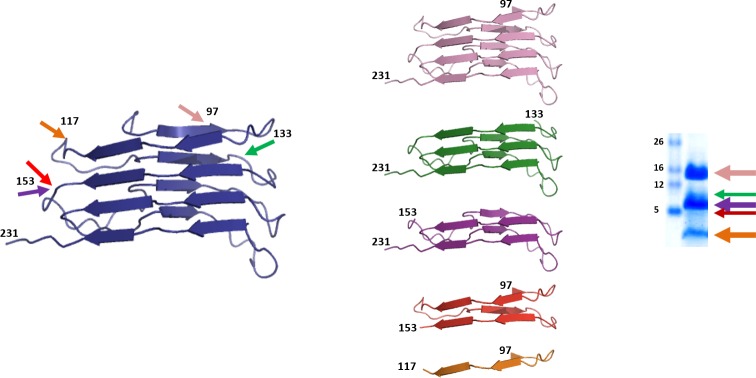
Fig 11. Graphical representation of the PrP fragments identified after PK-digestion of L-seeded-PMSA by epitope mapping and ESI-TOF and their origin based on the 4 rung β-solenoid model for PrPSc.
The identification of the main proteolytic fragments of L-seeded-PMSA after PK digestion (characteristic whole PK-resistant core after amino terminal digestion represented in blue, encompassing residues 89–231) by epitope mapping and ESI-TOF showed four major cleavage sites at positions ~97, ~117, ~133 and ~153 that give rise to five fragments of ~15 (pink, encompassing residues ~97–231, rungs 1 to 4), ~11 (green, encompassing residues ~133–231, rungs 2/3 to 4), ~9 (purple, encompassing residues ~153–231, rungs 3 and 4), ~6 (red, encompassing residues ~97–153, rungs 1 to 3) and ~2 (orange, encompassing residues ~97–117 rungs 1 and 2) kDa. Based on the assumption that PK cleaves accessible and flexible sites of the protein, most likely loops linking β-strands, the main fragments and cleavage sites may indicate that the overall structure of L-seeded-PMSA could fit with the 4-rung β-solenoid model proposed previously for brain-derived prions [34].