Fig. 9.
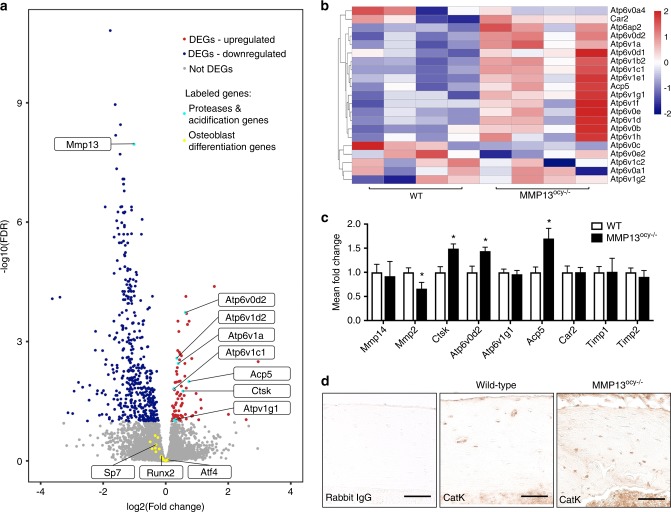
Osteocyte deficiency of MMP13 causes dysregulation of genes related to matrix degradation and acidification. a RNA-seq of wild-type and MMP13ocy−/− mice (n = 4) identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) that are significantly repressed (blue) or induced (red) in MMP13ocy−/− bone, with downregulation of MMP13 and upregulation of several proteases and acidification-related genes (highlighted in turquoise). Transcription factors and other genes implicated in osteoblast differentiation (yellow) are among the genes that did not show significant expression differences in MMP13ocy−/− bone (gray). b Genes related to acidification were hierarchically clustered in a heatmap by z-score. c qPCR of wild-type (n = 8) and MMP13ocy−/− (n = 6) bone validates both co-regulated and compensatory expression of PLR genes (mean ± SD). d Immunohistochemistry reveals increased levels of Cathepsin K in osteocytes in MMP13ocy−/− cortical bone (scale bars 50 μm). *P < 0.05 between genotypes by unpaired t test