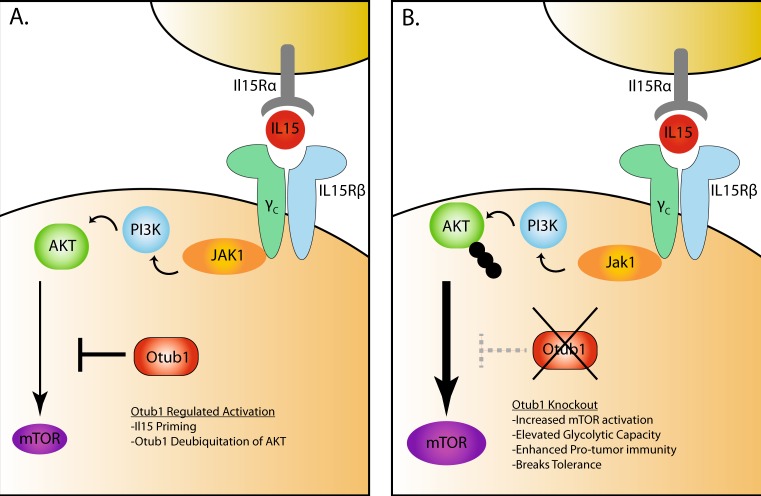
Fig. 1.
Otub1-mediated regulation of the IL-15 signaling pathway. a The heterodimeric IL-15Rβ /common γ chain (γc) receptor complex on CD8 T cells and NK cells recognizes IL-15 in complex with IL-15Rα from IL-15-producing cells. Engagement of the IL-15 receptor complex initiates a number of signaling cascades, including activation of PI3K. Ubiquitinated AKT is recruited to the membrane surface, where it activates mTOR, leading to downstream changes in cellular activation. Zhou et al. showed that Otub1 negatively regulates the IL-15 signaling pathway by deubiquitinating AKT, limiting mTOR activation. b When Otub1 is removed from CD8 T cells and NK cells, this pathway is left unchecked and causes increased signaling through mTOR. Otub1-deficient cells have enhanced effector function and clear pathogens and tumors more effectively. Otub1 KO also causes a break in self-tolerance and increases susceptibility to autoimmunity. Changes in Otub1-deficient cells are dependent upon intact IL-15 signaling