Figure 3.
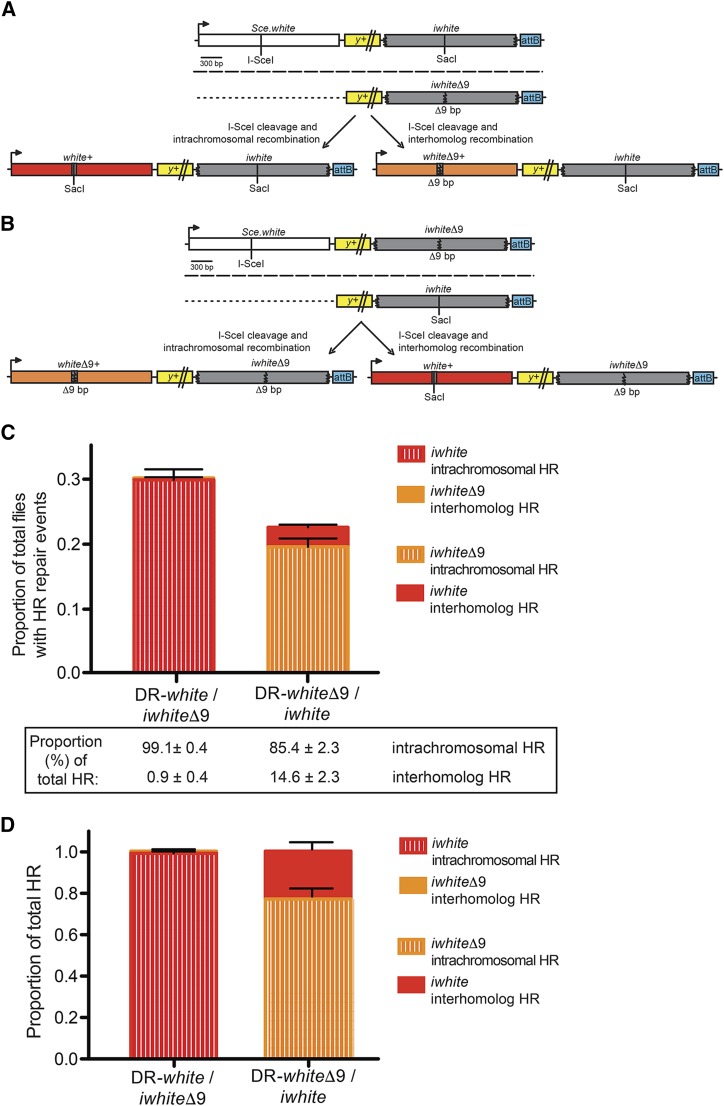
Intrachromosomal HR repair is preferred over interhomolog HR repair in mitotically dividing cells. (A) The intrachromosomal/interhomolog choice repair assay. Females carrying DR-white are crossed with males carrying the iwhiteΔ9 homolog donor template. HR repair of an I-SceI induced DSB from the intrachromosomal iwhite donor template results in gene conversion of the Sce.white sequence to white+ (red box), resulting in red-eyed progeny. HR repair from the interhomolog iwhiteΔ9 donor template results in gene conversion of the Sce.white sequence to whiteΔ9+ (orange box), resulting in orange-eyed progeny. Homologs are separated by long dashed line; dotted lines are used for direct comparison with other figures. (B) The same intrachromosomal/interhomolog choice repair assay is performed with flies carrying DR-whiteΔ9 and an iwhite homolog donor template. Intrachromosomal HR repair results in gene conversion of the Sce.white sequence to whiteΔ9+ (orange box), while interhomolog HR repair results in gene conversion to white+ (red box). (C) F2 progeny of 79 individual male germlines of DR-white/iwhiteΔ9 and 63 individual male germlines of DR-whiteΔ9/iwhite were scored. Average HR frequency out of total flies scored is shown. Error bars are S.E.M. Values given below are proportion of intrachromosomal or interhomolog HR out of total HR events ± SEM (D) Proportion of intrachromosomal (striped bars) or interhomolog (solid bars) HR out of total HR repair events in either DR-white/iwhiteΔ9 or DR-whiteΔ9/iwhite whole adult flies using TIDE analyses. Error bars are S.E.M.