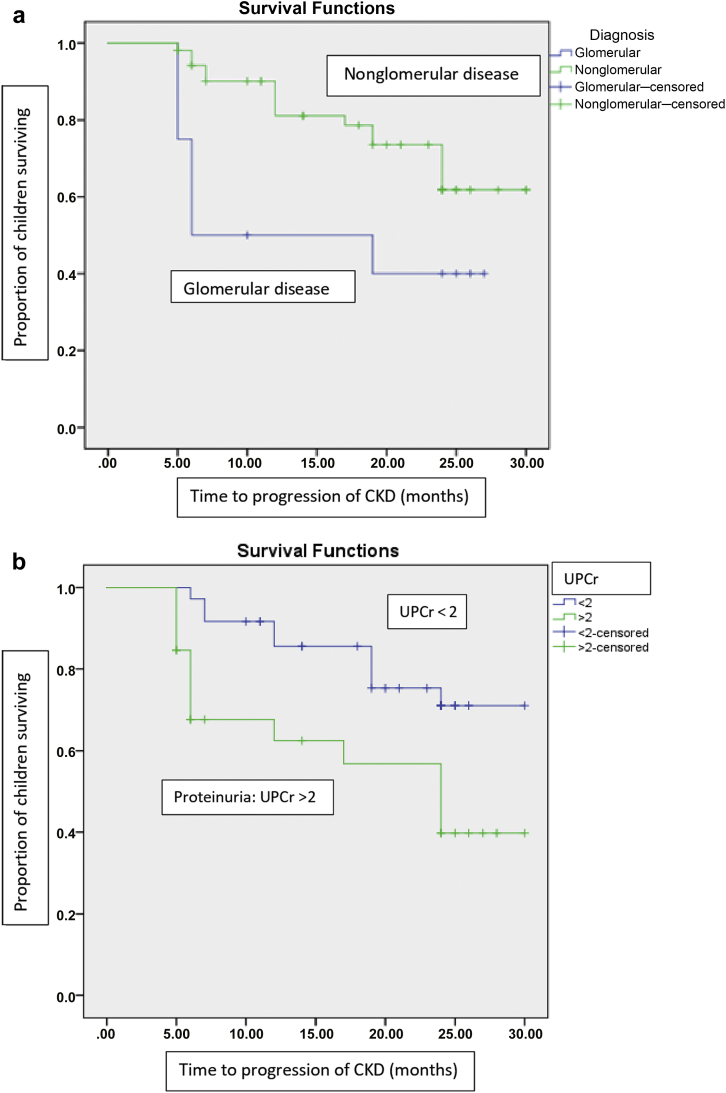
Figure 2.
(a) The survival analysis showing time to progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in children with glomerular disease in comparison to those with nonglomerular disease. Children with glomerular disease had a higher risk of progression when compared to those with nonglomerular disease (hazard ratio 2.59, 95% confidence interval 1.07, 6.27, P = 0.034). (b) Survival analysis comparing time to progression of CKD among children with proteinuria (urine protein-to-creatinine ratio [UPCr] > 2) and those without proteinuria. UPCr > 2 at baseline was associated with the risk of progression of CKD (hazard ratio 3.1, 95% confidence interval 1.33, 7.23, P = 0.009).