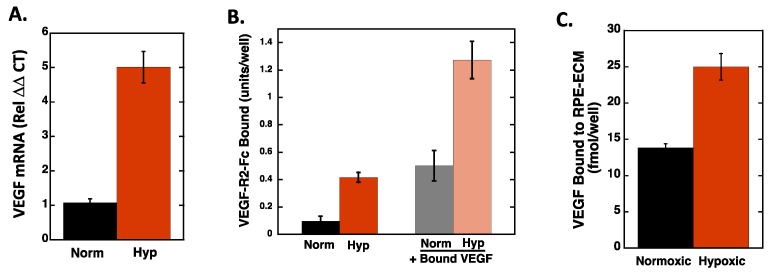
Figure 3.
Hypoxia increases VEGF expression, VEGF deposition in the ECM, and VEGF binding in RPE cells. RPE cells were subjected to normoxia and hypoxia for 72 h. (A) Total RNA was extracted from RPE cells and mRNA quantified using qPCR analyses, as described in Materials and Methods. The data is normalized to the 18S RNA and to the normoxic control for each condition and expressed as the average ± SEM. (N = 4; n = 2). (B) After the normoxic/hypoxic conditioning, RPE cells were washed and incubated with and without 50 ng/mL VEGF for 1 h at 4 °C. Unbound VEGF was removed from the cells by washing and the cells were subsequently incubated with Fc-VEGFR2 Chimera. Bound Fc-VEGF-R2 was detected with an HRP-linked secondary antibody. The data are expressed as average background corrected absorbance values ± SD (N = 4). (C) 125I-VEGF was bound to normoxia/hypoxia were RPE cells and the amount bound to the ECM extracted and quantitated. Data represent the average ± SD of quadruplicate wells (N = 4). Hypoxia induced a statistically significant increase in VEGF mRNA (A), VEGFR2 binding (B), and VEGF increased VEGFR2 binding to both normoxic and hypoxic cells (B), and hypoxia increased VEGF binding to the ECM of RPE cells.