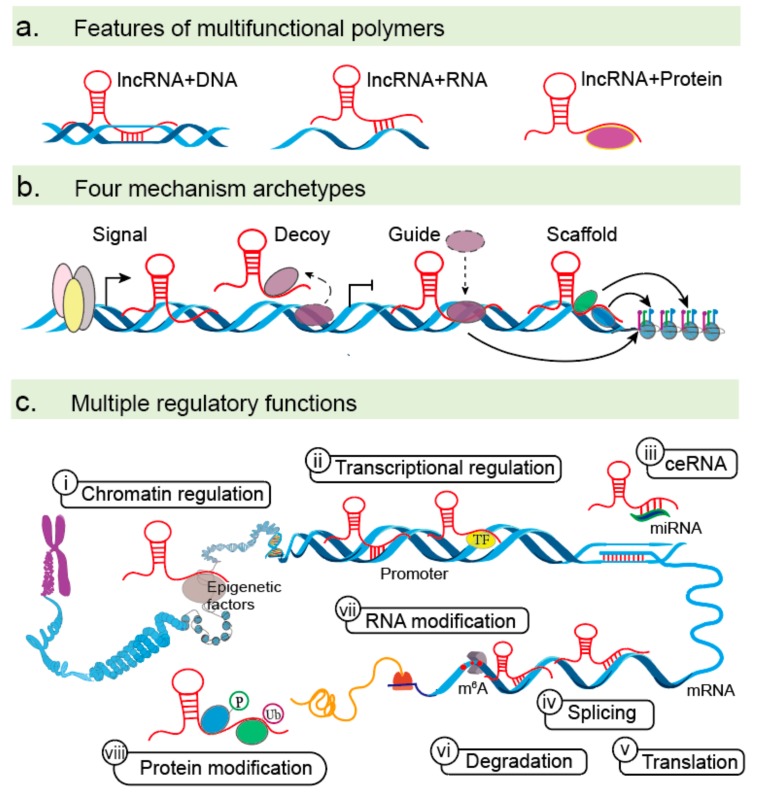
Figure 1.
LncRNA functions. (a) lncRNAs can bind DNA, RNA, and protein molecules to regulate gene expression at multiple levels via base pairing or secondary structure formation. (b) LncRNAs have four primary roles as signals, decoys, guides, and scaffolds. (c) Mechanism of action for lncRNAs in the nucleus (i–ii) and cytoplasm (iii–viii). (i) LncRNAs can recruit epigenetic factors to change patterns of chromatin organization, (ii) activate or repress the transcription of certain genes by interacting with DNA sequences or TFs, (iii) act as ceRNAs by base pairing with miRNA and diminishing its inhibitory effects, and manipulate mRNA function by base pairing to (iv) regulate alternative splicing (e.g., MALAT 1), (v) affect mRNA translation (e.g., TTN-AS1 and AC132217.4), and (vi) mRNA degradation (e.g., CASC11). (vii–viii) lncRNAs can modify mRNA and proteins, playing regulatory roles in methylation, phosphorylation, and ubiquitination.