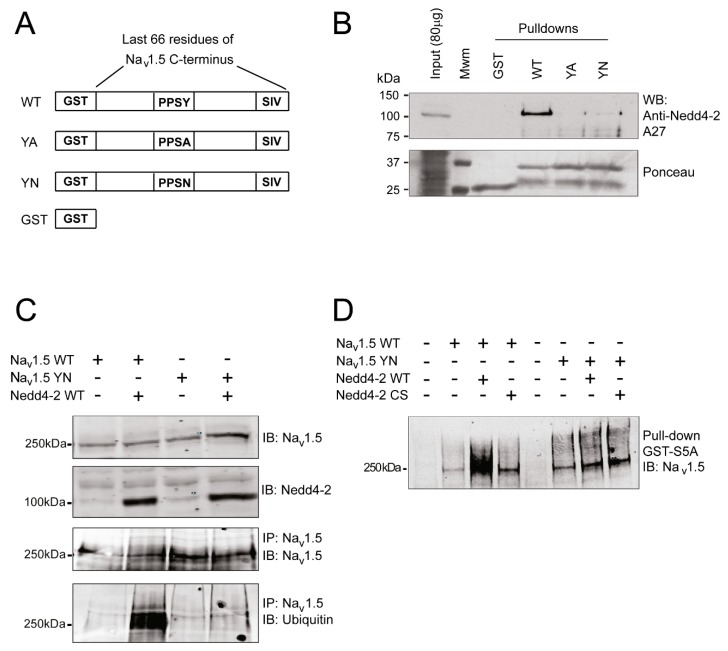
Figure 1.
The SCN5A-p.Y1977N mutation abolishes the interaction between Nav1.5 and Nedd4-2 and Nedd4-2 ubiquitylation of Nav1.5. (A) Schematic representation of the four fusion proteins used for the pull-down experiments described in (B). PPSY (proline-proline-serine-tyrosine) represents the wild-type (WT) sequence of the PY-motif of Nav1.5, while PPSA and PPSN represent mutations of the tyrosine (Y) of the PY-motif in alanine (A) and asparagine (N), respectively. (B) Western blots of pull-down fractions performed on HEK293 lysates against Nedd4-2. The bottom panel shows a Ponceau staining of a representative nitrocellulose membrane, showing the presence of Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) fusion proteins for the different pull-down experiments. (C) Immunoprecipitation of Nav1.5 followed by blotting against either Nav1.5 or ubiquitin demonstrating ubiquitylation of the WT channel, but not of the YN channel, in the presence of Nedd4-2 WT. (D) Total ubiquitylated proteins from HEK293 lysates precipitated using GST-S5A fusion proteins and subsequently blotted with an antibody against Nav1.5, demonstrating a lack of WT Nav1.5 ubiquitylation in the presence of a catalytic inactive form of Nedd4-2 (Nedd4.2 CS) as well as absence of ubiquitylation of YN Nav1.5 in the presence of WT Nedd4-2. Data were collected from three experiments.