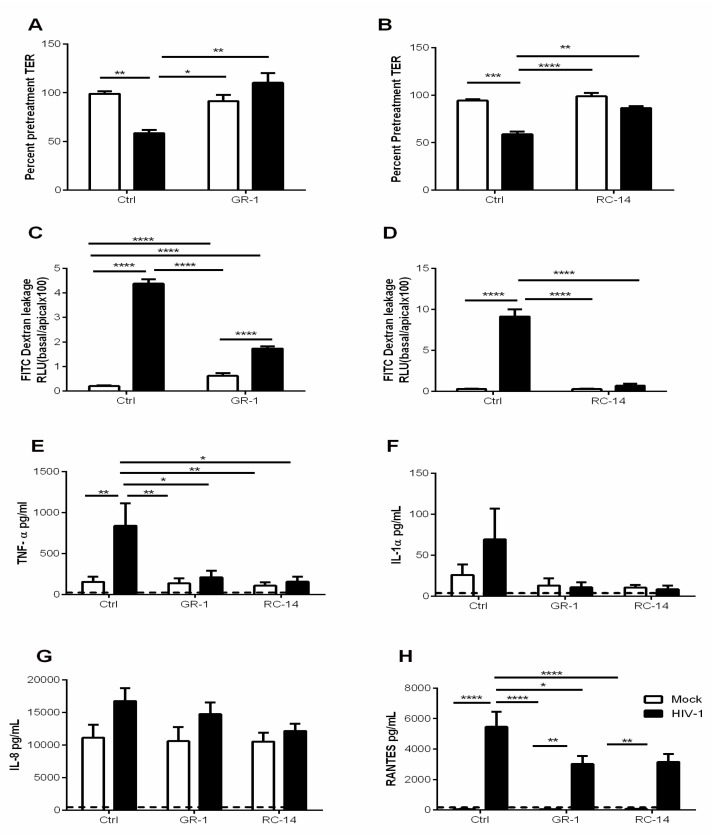
Figure 3.
Probiotic strains of lactobacilli ameliorate HIV-1-mediated barrier disruption and downregulate proinflammatory cytokine production by GECs. GECs were treated for 2 h with probiotic strains L. rhamnosus GR-1 and L. reuteri RC-14 abbreviated GR-1 and RC-14 respectively or no bacteria (Control). Following treatment, various cultures of GECs were then exposed to HIV-1 or no virus (Mock) and monitored for 24 h. (A,B) TER values were observed pre- and 24 h post-HIV-1 exposure. TER is expressed as percent of TER measured before HIV-1 exposure. (C,D) Following treatment with lactobacilli and during viral exposure, GEC cultures were treated apically with FITC-labeled dextran dye. At 24 h, 50 µL of basolateral were collected and fluorescence was measured using a microplate reader. The dextran leakage in the basolateral compartment is expressed as a percentage of dextran added to the apical compartment. (E–H) 24 h post-exposure to HIV-1, cell supernatants were collected and analyzed for TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-8, and RANTES. Dashed line indicates assay limit of detection. Data shown is representative of 6–9 separate experiments done on cells isolated from 6–9 different tissues, each experiment had 3 replicate cultures for each experimental condition. Data is plotted as mean + SEM. Statistical significance is indicated: **** p < 0.0001, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05.