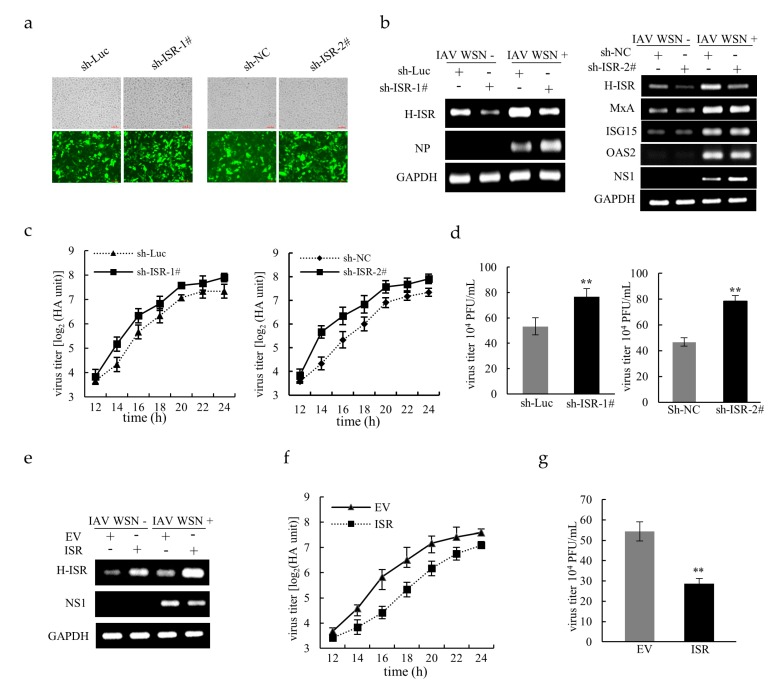
Figure 3.
LncRNA ISR suppresses IAV replication. (a) Optical and their corresponding fluorescence images of A549 cells stably expressing pSIH-H1-GFP vectors targeting lncRNA ISR or luciferase control (Luc) or scramble nucleotide sequences (NC) (100 μm); (b) The A549 cells expressing two different sequences of lncRNA ISR-silencing shRNAs (sh-ISR-1# and sh-ISR-2#) or sh-Luc or sh-NC were infected with or without IAV WSN [MOI = 0.8 (left) MOI = 0.4 (right)] for 16 h. After infection, total RNA was extracted for RT-PCR to detect lncRNA ISR or ISGs (MxA, ISG15 and OAS2) expression. RT-PCR for detecting viral NP or NS1 was performed to indicate the extent of viral replication. The cell culture supernatants were harvested at the indicated times for hemagglutination assay (c) and at 14 hpi for plaque assay (d) to measure virus titers. Data are represented as mean ± S.D. ** p < 0.01; (e) The A549 cells carrying either lncRNA ISR-expressing plasmid or EV were infected with or without IAV WSN (MOI = 0.4) for 16 h. After infection, total RNA was extracted for RT-PCR to detect lncRNA ISR expression. The cell culture supernatants were harvested at the indicated times for hemagglutination assay (f) and at 16 hpi for plaque assay (g) to measure virus titers. Data are represented as mean ± S.D. ** p < 0.01.