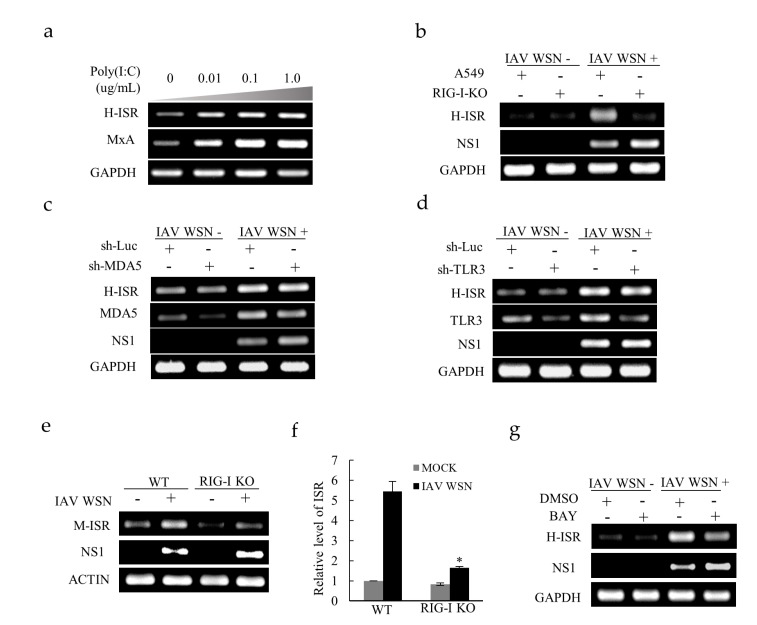
Figure 4.
IAV-induced lncRNA ISR expression is regulated by RIG-I-dependent signaling. (a) A549 cells were treated with poly (I:C) at indicated concentrations for 4 h. RT-PCR was performed to determine lncRNA ISR expression; (b) A549 WT and A549 RIG-I-knockout (KO) cells were infected with or without IAV WSN (MOI = 0.8). At 16 hpi, total RNA was extracted for RT-PCR to detect lncRNA ISR expression; (c) The expression levels of lncRNA ISR in MDA5 knockdown and sh-Luc control cells infected with or without IAV WSN (MOI = 0.8) were determined by RT-PCR; (d) The expression levels of lncRNA ISR in TLR3 knockdown and sh-Luc control cells infected with or without IAV WSN (MOI = 0.8) were determined by RT-PCR; (e,f) C57BL/6 WT and RIG-I-KO mice were infected intranasally with or without 5 × 104 pfu of IAV WSN virus (n = 8 mice/group). At 24 hpi, the lungs were collected and subjected to RT-PCR (e) and qRT-PCR (f) to detect lncRNA ISR expression. Data are represented as mean ± S.D. * p < 0.05; (g) A549 cells were treated with 8 μM NF-κB inhibitor BAY 11-7082 (BAY), followed by infection with/without IAV WSN (MOI = 0.8). At 16 hpi, total RNA was analyzed by RT-PCR to determine lncRNA ISR expression.