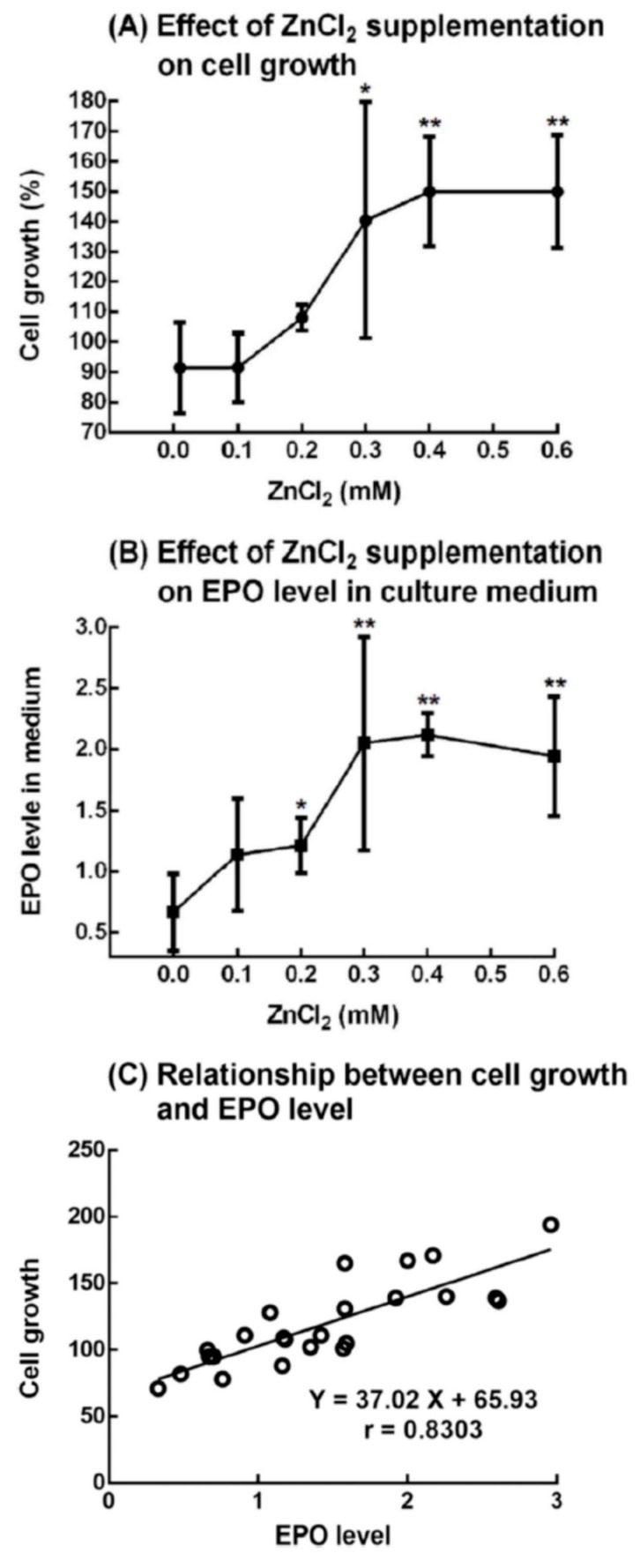
Figure 8.
Effect of ZnCl2 supplementation on the growth of 5.1-μm cells (immature reticulocytes) and production of EPO from rat bone marrow cells. Rat bone marrow cells in the medium and rat serum were suspension-cultured with different concentrations of ZnCl2. The group without the supplementation of ZnCl2 (zinc concentration in the medium = 0.01 mM) was referred to as the control group, and the ZnCl2-supplemented groups (zinc concentrations of 0.1 to 0.6 mM) were referred to as experimental groups. After 1 day, the cultured cells were harvested: (A) Effect of ZnCl2 supplementation on cell growth. The cell growth is expressed as the ratio of the number of 5.1-μm cells at day 1 to that at day 0. (B) Effect of ZnCl2 supplementation on EPO levels in the culture medium. The EPO level is expressed as the ratio of EPO concentration at day 1 to that at day 0. (C) Relationship between cell growth and EPO level. The results are the mean ± SD from four independent experiments. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01: Significant difference between the ZnCl2 supplemented and control groups (n = 4).