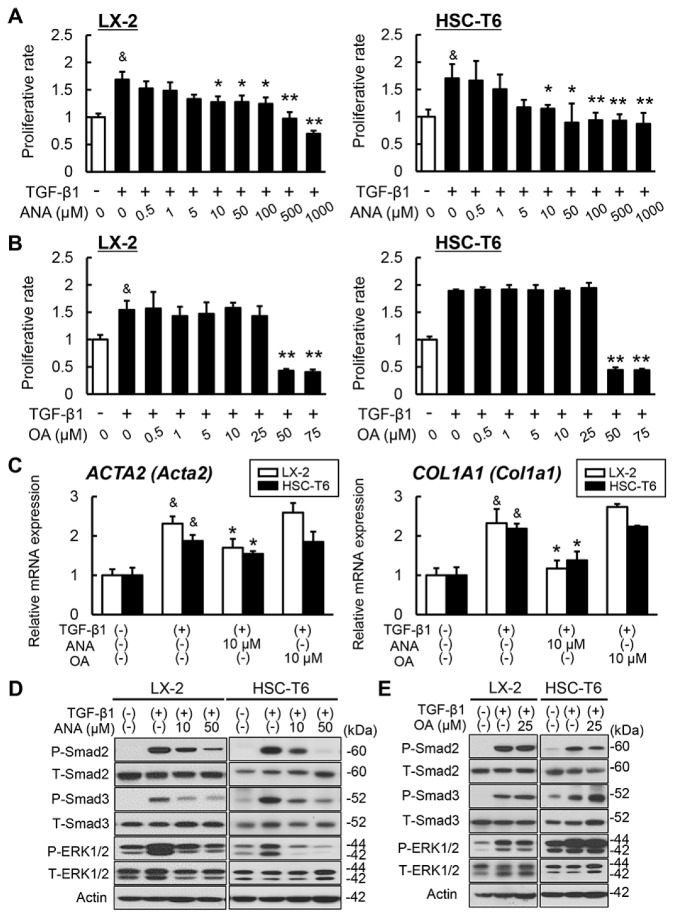
Figure 5.
Effects of oleanolic acid and anagliptin in vitro hepatic stellate cells. (A,B) The effects of anagliptin (ANA) (A) or oleanolic acid (OA) (B) on the TGF-β1-stimulated proliferation of LX-2 and HSC-T6 cells. Both cell lines were cultured with different concentrations of ANA or OA for 24 h. The proliferative rate is the ratio to control group cultured without TGF-β1 and ANA or OA. (C) The effects of anagliptin (ANA) or oleanolic acid (OA) on the mRNA expressions of ACTA2 (Acta2) and COL1A1 (Col1a1) in the TGF-β-stimulated LX-2 and HSC-T6 cells. Both cell lines were cultured with 10 μM of ANA or OA for 24 h. Quantitative values are relatively indicated as ratios to the values of ANA(–)/OA(–)-group. The mRNA expression levels were measured by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR), and Gapdh was used as internal control for qRT-PCR. (D,E) Western blots of whole cell lysates from LX-2 and HSC-T6 for the phosphorylation of Smad2, Smad3, and ERK1/2. The cells were cultured with and/or without TGF-β and ANA (D) or OA (E). Actin was used as internal control for western blotting. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 8). &, P ≤ 0.01 compared with TGF-β1(–)/ANA(–)/OA(–)-group; *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01 compared with TGF-β1(+)/ANA(–)/OA(–)-group.