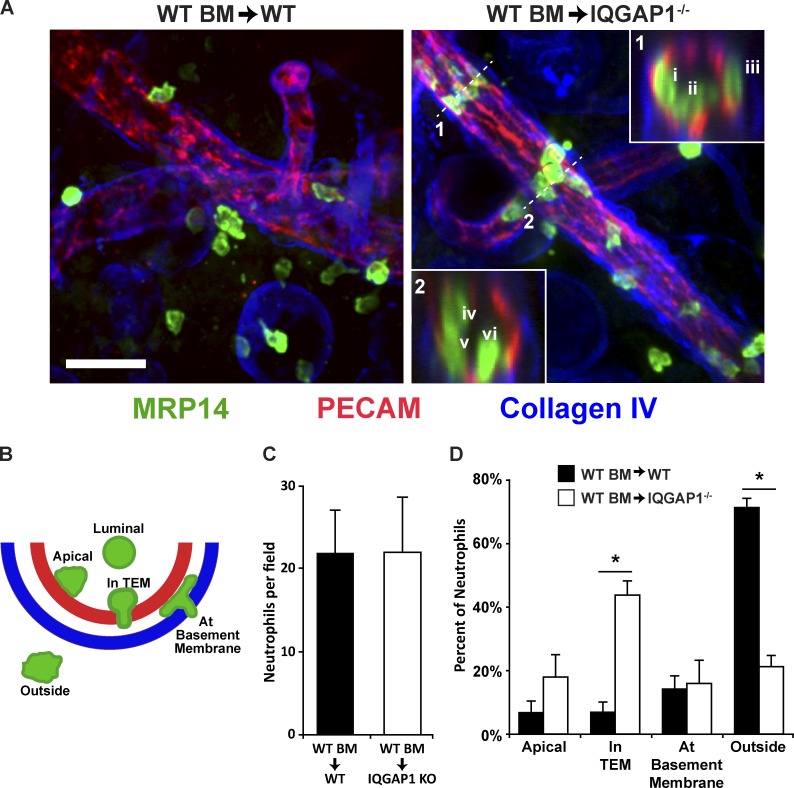
Figure 9.
IQGAP1 is required for neutrophil TEM in vivo. (A) IQGAP1 knockout and WT mice were lethally irradiated and their bone marrow reconstituted from WT donors as described in Materials and methods. After allowing reconstitution of the mice, one ear of each mouse was treated topically with croton oil in an acetone/olive oil carrier while the other ear received the carrier only. After 5 h, the mice were sacrificed and their ears processed for immunofluorescence imaging using confocal microscopy. Representative images from WT (WT BM → WT) and IQGAP1 knockout (WT BM → IQGAP1−/−) are shown. Neutrophils were visualized with an antibody against MRP14 (green), the vessel and junctions were detected using anti-PECAM, and the basement membrane was visualized using anti-Collagen IV. Insets show the orthogonal view at position denoted by the dashed line. Orthogonal inset 1 shows one leukocyte in TEM (i), one apical (ii), and one at the basement membrane (iii). Orthogonal inset 2 shows one leukocyte on the apical surface (iv) and two that are in TEM (v and vi). Scale bar represents 50 µm. (B) Schematic of the positional scoring system used to quantify the neutrophil locations observed in A. (C) Quantitation of the total number of neutrophils per field. Only neutrophils within 50 µm of the vessel were scored. (D) Quantitation of the leukocyte positions from the images collected in A. Data shown were collected from two separate experiments, each of which contained at least two mice per condition. At least five fields (corresponding to ≥100 neutrophils) for each mouse were analyzed (n = 5 for WT recipients and n = 6 for the IQGAP1−/− recipients). Data shown are the average of the averages for each mouse and do not include data for the neutrophils found in the luminal position. *, P < 0.01. Carrier-only ears showed no signs of inflammation; neutrophils were rarely found in the tissue or associated with vessels (data not shown).