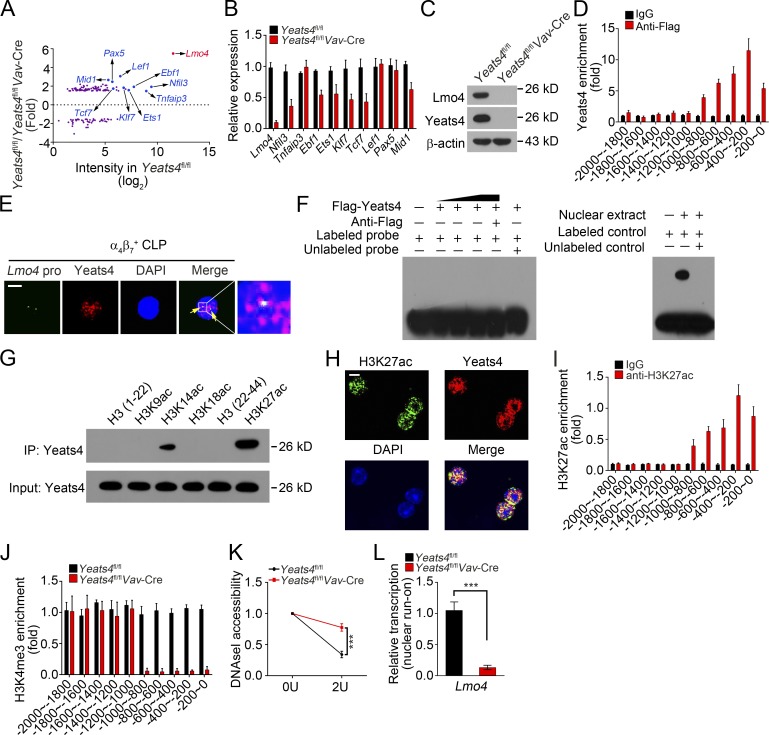
Figure 4.
Yeats4 initiates Lmo4 expression in α4β7+ CLPs. (A) Differentially expressed TFs in α4β7+ progenitors (Lin−CD127+c-KitintSca-1intα4β7+) from Yeats4fl/fl and Yeats4fl/flVav-Cre mice by microarray analysis. (B) qRT-PCR analysis for mRNA levels of indicated top 10 down-regulated TFs in α4β7+ CLPs from Yeats4fl/fl and Yeats4fl/flVav-Cre mice. (C) Protein levels of Lmo4 were tested by immunoblotting in α4β7+ progenitors (Lin−CD127+c-KitintSca-1intα4β7+) from Yeats4fl/fl and Yeats4fl/flVav-Cre mice. (D) Yeats4 enrichment on Lmo4 promoter was determined. α4β7+ progenitors (Lin−CD127+c-KitintSca-1intα4β7+) were isolated from Yeats4fl/fl and Yeats4fl/flVav-Cre mice, followed by ChIP assay. (E) Yeats4 was colocalized with the Lmo4 promoter by FISH assay. Scale bar, 5 µm. (F) EMSA for detection of direct interaction between Yeats4 and the Lmo4 promoter. The Lmo4 promoter was biotin labeled. Positive control probes interacted with nuclear extract (right panel). (G) Pull-downs were performed using Flag-Yeats4 and biotinylated histone peptides with different modifications, followed by immunoblotting with anti-Flag antibody. IP, immunoprecipitation. (H) Colocalization between Yeats4 and H3K27ac in α4β7+ CLPs was assessed by immunofluorescence staining. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bar, 5 µm. (I) Analysis of H3K27ac enrichment on Lmo4 promoter using ChIP-qPCR assay. (J) Enrichment of H3K4me3 on Lmo4 promoter in αLPs was analyzed by ChIP analysis. (K) DNase I accessibility assay of Lmo4 promoter in α4β7+ progenitors (Lin−CD127+c-KitintSca-1intα4β7+) from Yeats4fl/fl and Yeats4fl/flVav-Cre mice. (L) α4β7+ progenitors (Lin−CD127+c-KitintSca-1intα4β7+) from Yeats4fl/fl and Yeats4fl/flVav-Cre mice were subjected to nuclear run-on assay, followed by RT-PCR analysis for Lmo4 transcription. ***, P < 0.001 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. All data are representative of at least three independent experiments and are expressed as mean ± SD.