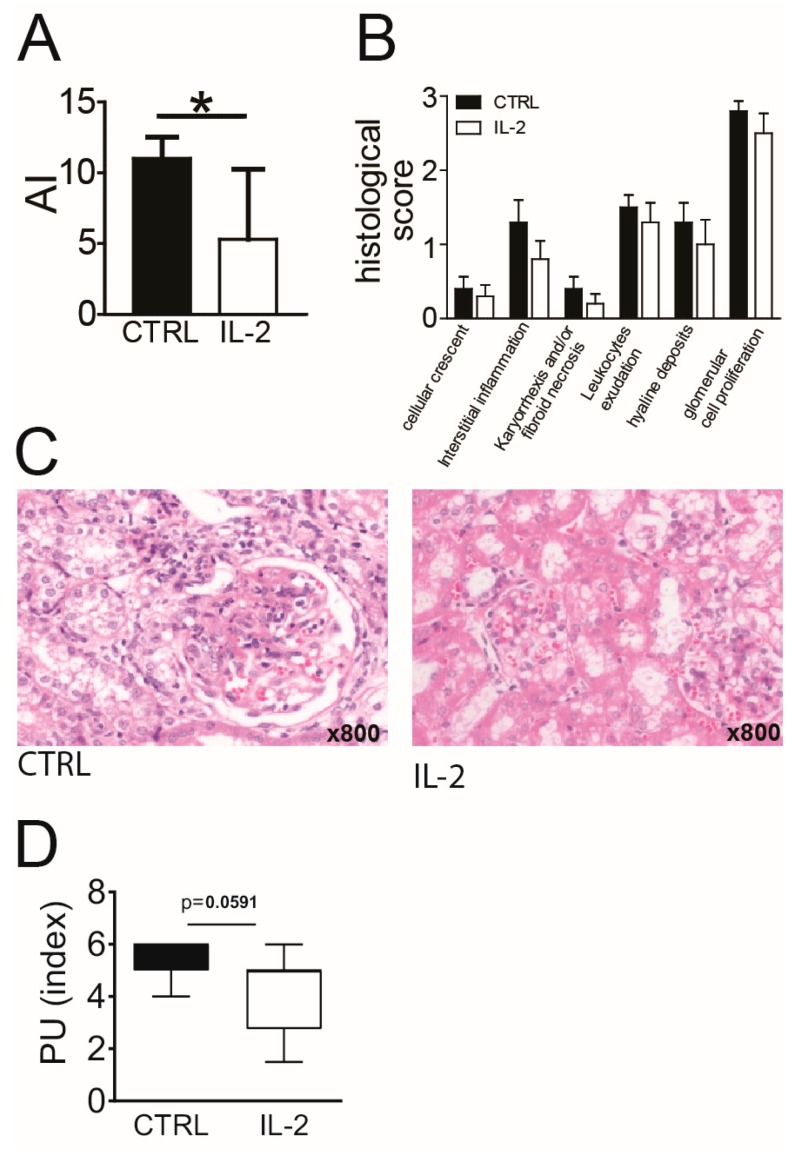
Figure 6.
Long-term IL-2 treatment reduces nephritic activity at a histological level. (A) The renal activity index (AI) was determined in single kidneys from (NZB × NZW) F1 mice with established nephritis at day 31 after the initiation of the IL-2 treatments (48 h after the last IL-2 injection; IL-2, white bars) and compared to PBS-treated control mice (CTRL, black bars). (B) The six differentially weighted histomorphological scores according to the AI are shown for the control and the IL-2 treated group. (C) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin stained kidney sections from either controls (left) or from IL-2 treated mice (right) are shown. (D) The proteinuria index of controls and IL-2 treated mice at day 31 are shown. Data represent the mean + SD of the scores summarized from two to five independent experiments (n = 6–17). Mann-Whitney U test was used for statistical analyses (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01). One outlier in the CTRL group at d0 was identified and removed after using the ROUT test.