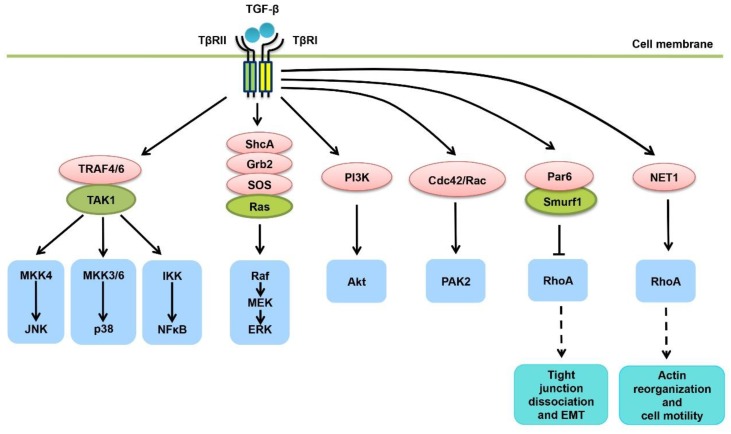
Figure 2.
TGF-β activates versatile non-Smad pathways. Ligand-bound TGF-β receptors activate TAK1 by associating with TRAF4/6, resulting in activation of the MKK4-JNK, MKK3/6-p38 or IKK-NFκB signaling cascades. TβRI is able to phosphorylate the adaptor protein ShcA at both serine and tyrosine residues, causing activation of Ras/ERK MAPK signaling. TGF-β receptors could also interact with p85, the regulatory subunit of PI3K, leading to activation of PI3K/Akt signaling. In addition, TGF-β receptors may induce a rapid activation of the small GTPases Cdc42/Rac, and subsequent activation of PAK2 kinase. RhoA has been shown as an important mediator of TGF-β in different contexts, contributing to actin reorganization and cell motility. Intriguingly, TGF-β receptors could induce a localized and ubiquitin-mediated degradation of RhoA in tight junctions, through TβRII-induced phosphorylation of Par6 and recruitment of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1, leading to EMT induction.