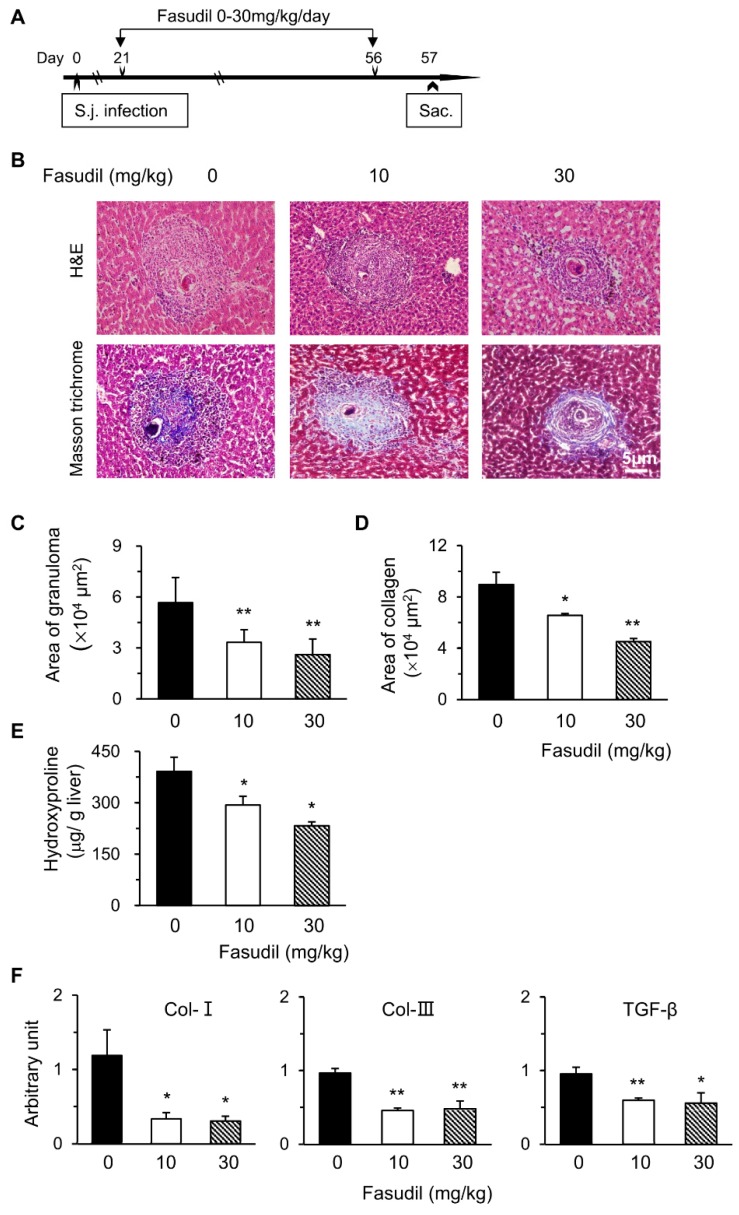
Figure 1.
Fasudil therapy suppresses hepatic granuloma formation and fibrosis in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum. (A) Female C57BL/6 mice were infected with S. japonicum (S.j.) and injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with fasudil at 0, 10, and 30 mg/kg body weight daily for 5 weeks (day 21–56). Mice were sacrificed 24 h after the last injection. (B) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson trichrome staining are shown in liver sections. The sizes of (C) granulomas and (D) collagen areas by Masson trichrome staining around a single egg were measured. (E) Hepatic hydroxyproline levels were assayed. (F) The mRNA levels of collagen type I (Col-I), Col-III, and transforming growth factor-1 (TGF-β1) in liver tissues were determined using real-time PCR. Data are normalized to an 18S reference and expressed as arbitrary units. Results are representative of three independent experiments (C–F, means + standard error (SE), n = 5–8). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. PBS-treated (fasudil 0) groups.