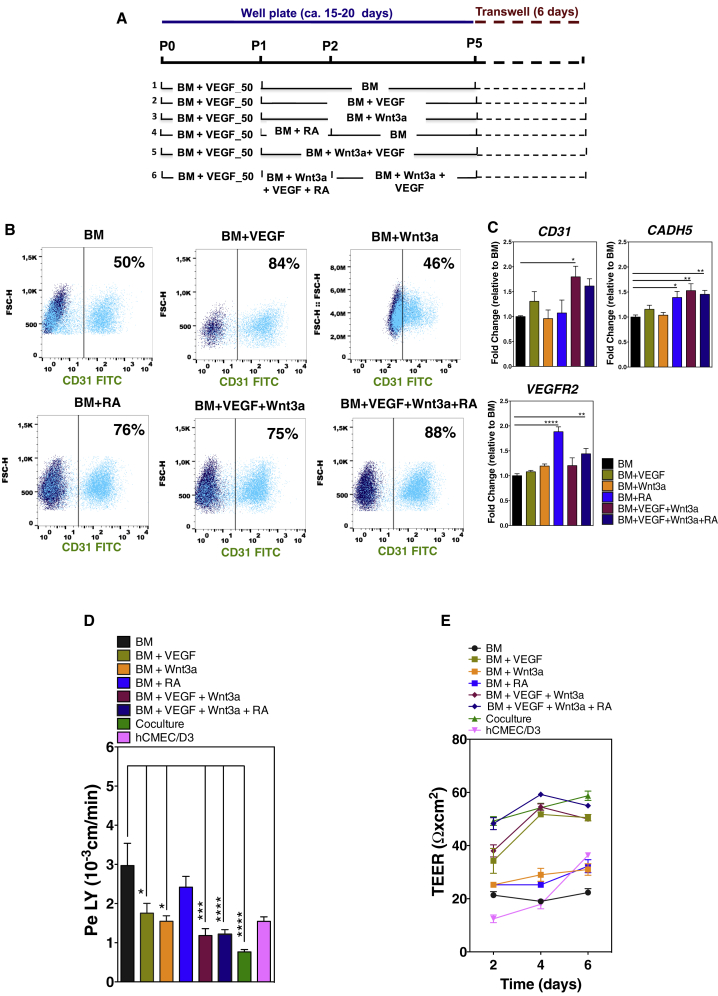
Figure 2.
Effect of Soluble Factors on the Specification of EPCs into BCLECs
(A) Schematic representation of the protocols used to specify CD31+ onto BCLECs.
(B) Expression of CD31 marker on ECs at passage 4 was assessed by flow cytometry. Percentages of positive cells were calculated based on the isotype controls (1%; dark blue scatter plot).
(C) Fold change of endothelial gene expression in ECs cultured in the different protocols at passage 4 (without purification) relative to ECs cultured in BM conditions. Genes were normalized against the control gene ACTB. Values are means ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiment, 3 technical replicates per experimental condition). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test.
(D and E) (D) Paracellular permeability to LY and (E) TEER in cells either exposed or not to the chemical factors with purification 6 days after being plated on Matrigel-coated Transwell inserts. In (D) and (E), the hCMEC/D3 cell line and human hematopoietic progenitor cell-derived ECs cocultured with pericytes for 6 days (coculture condition) (Cecchelli et al., 2014) were used as controls. Values are means ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments; at least 3 Transwell inserts per independent experiment and experimental condition). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test.
See also Figure S1.