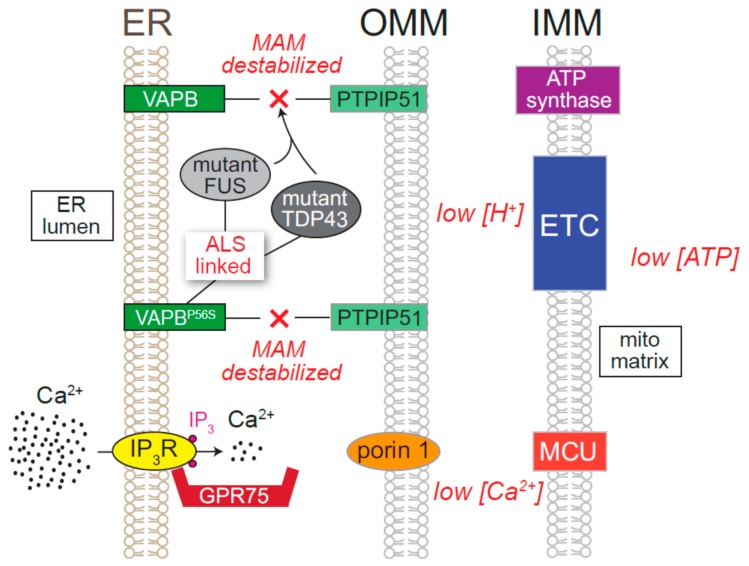
Figure 7.
Mechanisms of mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM) dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Various ALS-associated mutations lead to breakdown of MAMs. Mutated VAPB (VAPBP56S) leads to decreased binding with PTPIP51 and mutant FUS and TDP-43 disrupt the VAPB-PTPIP51 interaction, diminishing Ca2+ transfer from the ER to the mitochondria. Lower Ca2+ in the mitochondrial matrix results in less oxidative phosphorylation and reduced ATP production.