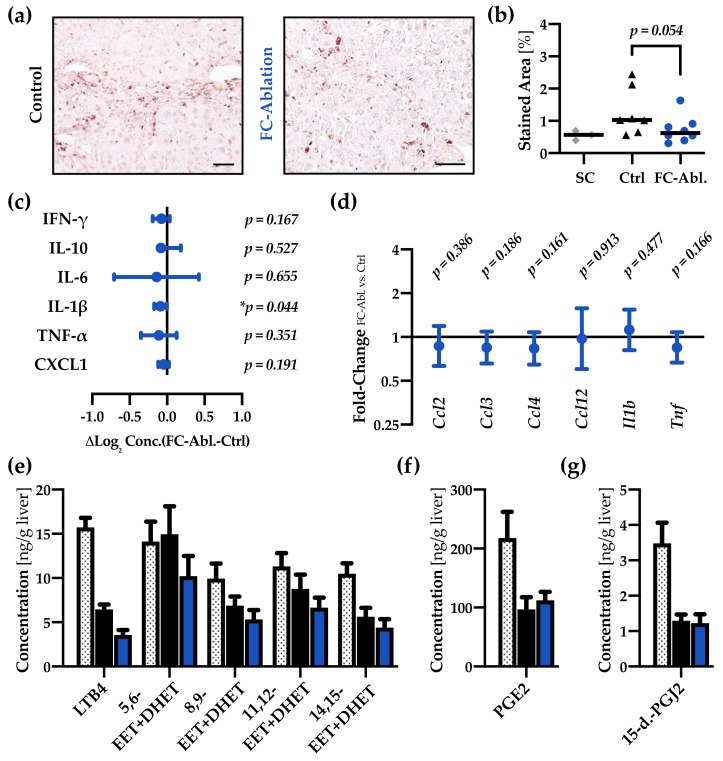
Figure 4.
Fibrocyte ablation lead to a reduction of hepatic IL-1β levels. (a) Immunohistochemical staining of CD45 (grey) and (b) subsequent morphometric analysis revealed a tendentially reduced number of leukocytes in the liver of fibrocyte-ablated mice. Magnification 200×, bar 50µm. Mann-Whitney U test was applied. (c) Multiplex ELISA demonstrated a reduction of IL-1β protein levels while none of the other cytokines were significantly regulated. Absolute concentrations and individual p-values are provided in Figure S8. (d) qRT-PCR showed no regulations in a panel of inflammatory genes (full data in Figure S5d–i). (e–g) In comparison to healthy supercontrols (n = 8, dotted bars), absolute quantification of hepatic eicosanoids revealed a notable decrease of all but one analyte (5,6-EET + DHET) in consequence of the TAA-treatment. The level of LTB4 is considerably lower in FC-ablated mice (n = 15, blue), compared to controls (n = 15, black). Mean of three measurements + SEM are depicted.