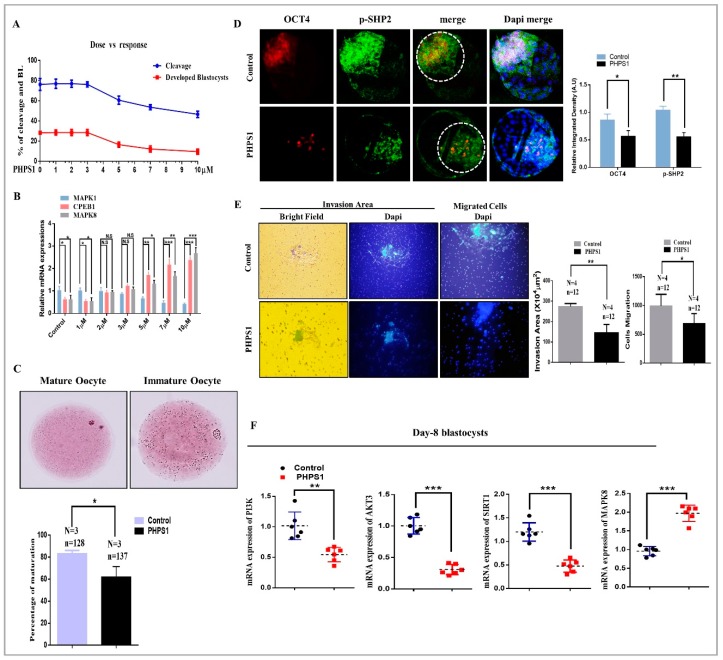
Figure 2.
The effects of SHP2 inhibition was analyzed during oocytes maturation and blastocysts development. (A) Dose dependent response of PHPS1 (SHP2 inhibitor) toward embryo cleavage and blastocysts development. (B) Dose dependent effect of PHPS1 on oocyte maturation pathways. Increase in PHPS1 concentration reduced mRNA expression of MAPK1, while CPEB-1 and MAPK8 showed upregulated expression (n = 20 per each group). (C) Aceto-orcein staining for detection of germinal vesical breakdown (GVBD) and first polar body (PB1) extrusion (oocyte maturation). Independent experimental repeat (N) and used oocytes (n) values are as indicated. SHP2 inhibition prevent oocyte maturation, indicating 62% maturation in PHPS1 group as compare to control vehicle-treated 83% maturation. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. Control and SHP2 inhibited blastocysts were immunolabeled with OCT4 (red) and SHP2 (green) and counter stained with DAPI to visualize DNA (Mean ± SEM). (D) Immunolocalization showing reduced OCT4 (red) and SHP2 (green) expression in PHPS1 treated blastocysts as compare to vehicle-treated control (n = 20 per each group). (E) The effects of SHP2 inhibition was checked for blastocysts implantation potential. Bright field showing area of invasion and DAPI for migrant cells in day-8 blastocysts. The invaded area and cellular migration were significantly lower in PHPS1 treated group as compare to control vehicle-treated group. Image J software was used to quantify the signal intensity of immunofluorescence images. (F) Genes related to survival and apoptosis were examined through qRT-PCR in day 8 blastocyst (n = 5). SHP2 inhibition significantly reduced the PI3K, AKT and SIRT expression, while substantially enhanced the apoptosis signaling related gene MAPK8 (JNK). The experiments were repeated 3 times and the data are shown here as a mean ± S.E.M. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.