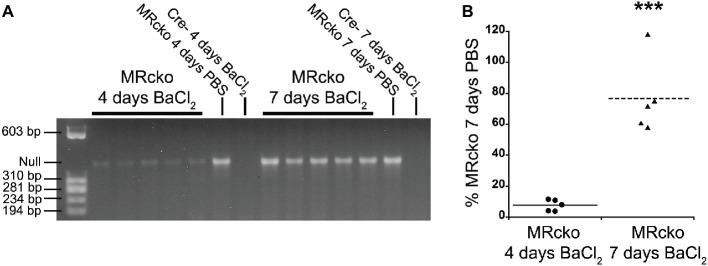
Figure 2.
Evaluation of MRcko excision after acute muscle injury. (A) PCR was run to detect the level of MR excision by presence of the MR null allele in TAs from mice at 4 (n = 5 MRcko barium chloride injection, n = 1 MRcko PBS injection, n = 1 Cre− barium chloride injection) and 7 (n = 5 MRcko barium chloride injection, n = 1 MRcko PBS injection, n = 1 Cre− barium chloride injection) (two technical replicates) days post-injury. (B) The level of MR null allele at 4 and 7 days post-injury was quantified and normalized to the level of MR null allele from PBS injection at 7 days post-injury. There was restoration of MR excision at 7 days post-injury (p = 0.0002). Means are shown by lines for each group in the dot plot. BaCl2, barium chloride injection; PBS, sterile phosphate buffered saline injection; TA, tibialis anterior; data were analyzed using a Student’s t-test; ***p ≤ 0.001 compared to MRcko barium chloride injection at 4 days post-injury.