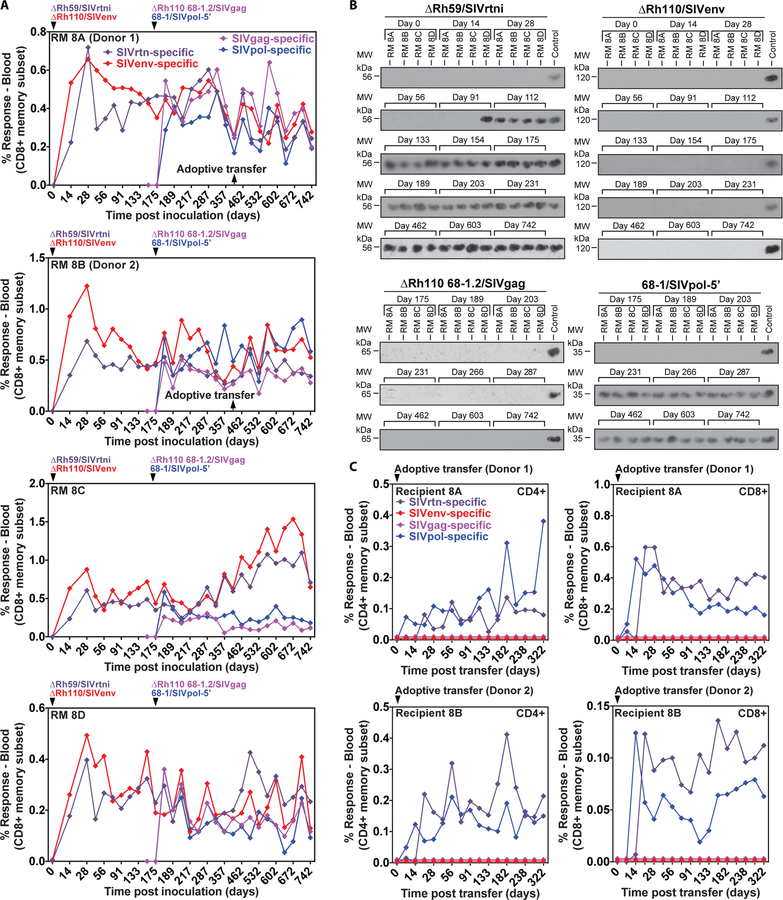
Figure 8: Comparison of the shedding and transmission upon leukocyte transfer of Rh110 (pp71)-deleted, Rh59 (UL35)-deleted and 68–1 RhCMV vectors.
(A) Four RMs were co-inoculated with 106 to 107 PFU of ΔRh59/SIVrtni, pentameric complex-repaired ΔRh110 68–1.2/SIVgag, ΔRh110/SIVenv, and 68–1/SIVpol-5’ at the designated time points and the CD8+ T cell responses to peptide mixes comprising each of the SIV antigens were longitudinally monitored in peripheral blood by flow cytometric ICS (CD69, TNFα, IFN-γ readout), with the response frequencies in the memory compartment shown (see also fig. S13B). (B) Immunoblots of viral co-cultures from urine samples obtained at the indicated days. Each of the SIV inserts carries a different epitope tag, allowing specific identification of each vector using tag-specific mAbs (see Materials and Methods). (C) Bone marrow and blood leukocytes from two of the RMs shown in A (1.9 × 107 bone marrow and 3.0 × 107 blood cells from RM 8A (donor 1); 0.8 × 107 bone marrow and 3.0 × 107 blood cells from RM 8B (donor 2); obtained at the indicated time point) were transferred to two naturally RhCMV+ (but vector-naïve) RMs to test the ability of leukocyte transfer to transmit each vector to a new host. Vector infection of the new host was determined by longitudinal assessment of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses to each of the four different SIV inserts, as described in (A).