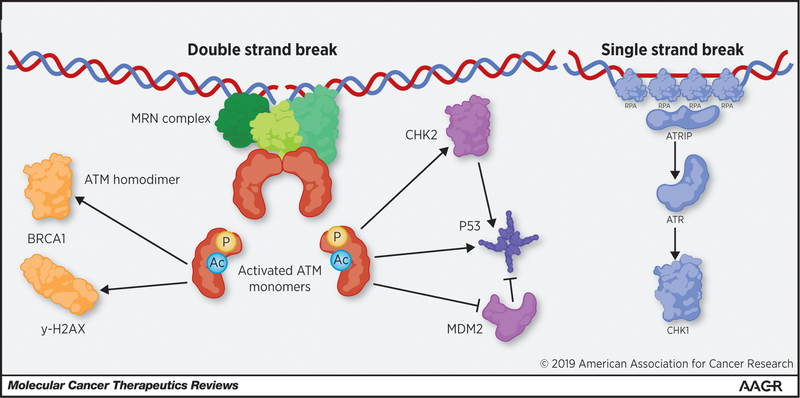
Figure 1: ATM functions and other related pathways for DNA repair.
ATM is recruited to DSBs by the MRN complex through direct interaction of NSB1 with ATM’s HEAT repeats. ATM is then activated through autophosphorylation, and acetylation by TIP60, this activation allows ATM to dissociate to the active monomeric state. ATM monomers can then signal for DNA repair through BRCA1 and γ-H2AX. ATM can also signal for cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis through the activation of p53 through direct phosphorylation and indirect activation through CHK2 and MDM2. In parallel, ATR is recruited to long stretches of single strand DNA caused by single strand breaks, the resection of DSBs, or replication stress. PARP1 is another factor that is critical for the repair of single strand breaks.