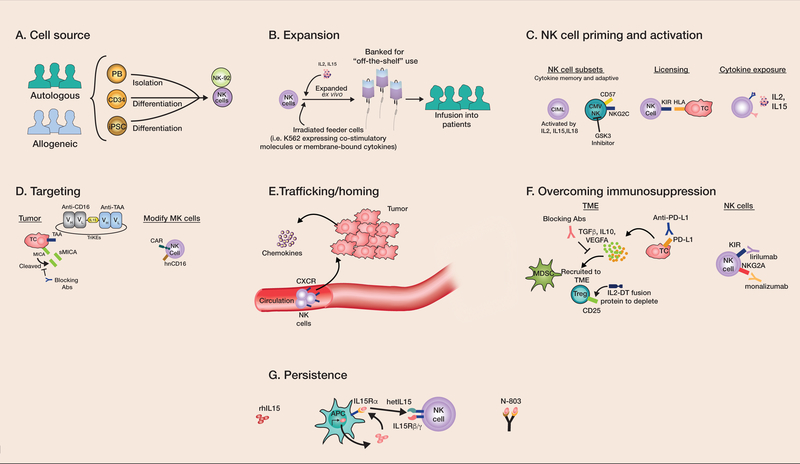
Figure 1: Strategies to improve NK cell immunotherapy.
(A) NK cells can be derived from autologous or allogeneic sources. Although most autologous NK cells are blood derived, allogeneic sources include PB NKs, CD34-, and iPSC-differentiated NK cells. PB NK: peripheral blood NKs; CD34: CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells; iPSC: induced pluripotent stem cells. (B) Ex vivo expansion is typically accomplished with cytokines such as IL2 or IL15, with many also incorporating irradiated feeder cells (typically using genetically modified K562 cells). The expanded NK cells can be used fresh or banked and frozen to be available on demand. To improve NK cell antitumor activity further, (C) cytokine-primed viral or small molecular–primed NK cells can be used, which include those with a memory phenotype, licensed subsets, and those generally exposed to gamma-chain cytokine activating cytokines. CIML: cytokine-induced memory-like; CMV-exposed NK: NK cells from cytomegalovirus seropositive individuals; GSK3: glycogen synthase kinase 3, KIR: killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, HLA: human leukocyte antigen. (D) Tumor targeting can be accomplished through increasing tumor expression of activating ligands (e.g. MICA) via upregulation or preventing cleavage. Tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) can also be targeted using therapeutic antibodies, engager molecules (e.g. tri-specific killer engagers (TriKEs)), and chimeric antigen receptors (CARs). sMICA: soluble MICA; hnCD16: high affinity, ADAM17 non-cleavable CD16. (E) Expression of chemokine receptors (like CXCL4) on NK cells can improve homing to tumor sites. (F) Strategies to overcome the immunosuppressive TME include blockade of inhibitory receptor interactions, interruption of negative immunoregulatory cytokines, and addressing suppressive immune cells such as Tregs and MDSCs through targeted depletion. IL-2-DT: IL2-diphtheria toxin fusion protein. (G) Improving NK cell persistence utilizing pro-survival and proliferative cytokines that do not stimulate Tregs, such as IL15 or modified versions (e.g. hetIL15, N-803), may mimic physiologic IL15 trans-presentation by antigen presenting cells (APCs). rhIL15: recombinant human IL15.