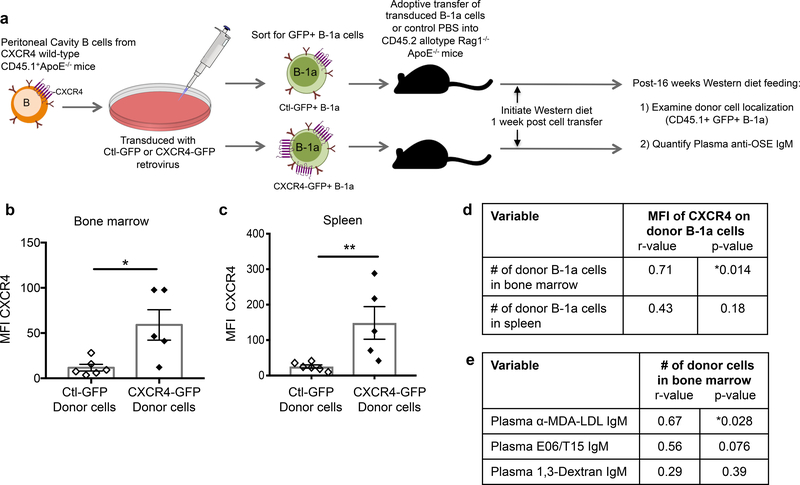
Figure 4. Overexpression of CXCR4 in murine B-1a cells associates with increased B-1a cell localization to the bone marrow and increased plasma anti-OSE IgM levels.
(a) Experimental setup: Peritoneal B cells from CXCR4 wild-type CD45.1 allotype ApoE−/− mice were transduced with CXCR4-GFP or Ctl-GFP retrovirus and 1×105 successfully transduced B-1a cells were intravenously transferred into Rag1−/−ApoE−/− hosts, which were fed 16 weeks of Western diet. Quantification of the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CXCR4 on recovered CD45.1+GFP+ donor B-1a cells in bone marrow (b) or spleen (c) of Rag1−/−ApoE−/− mice receiving CXCR4-GFP+ B-1a cells (n=5) or Ctl-GFP+ B-1a cells (n=6) after 16 weeks Western diet feeding. *P<0.05 or **P<0.01 by Mann-Whitney test. (d) The MFI of CXCR4 on donor B-1a cells correlated with the number of donor B-1a cells in bone marrow or spleen of Rag1−/−ApoE−/−recipient mice after 16 weeks Western diet feeding. N=11 mice. (e) The number of donor B-1a cells in bone marrow correlated with circulating levels of anti-MDA-LDL IgM, E06/T15 IgM specific for phosphocholine, or anti-1,3-Dextran IgM after 16 weeks Western diet feeding. Data presented as correlation coefficient (r) and statistical significance (p).