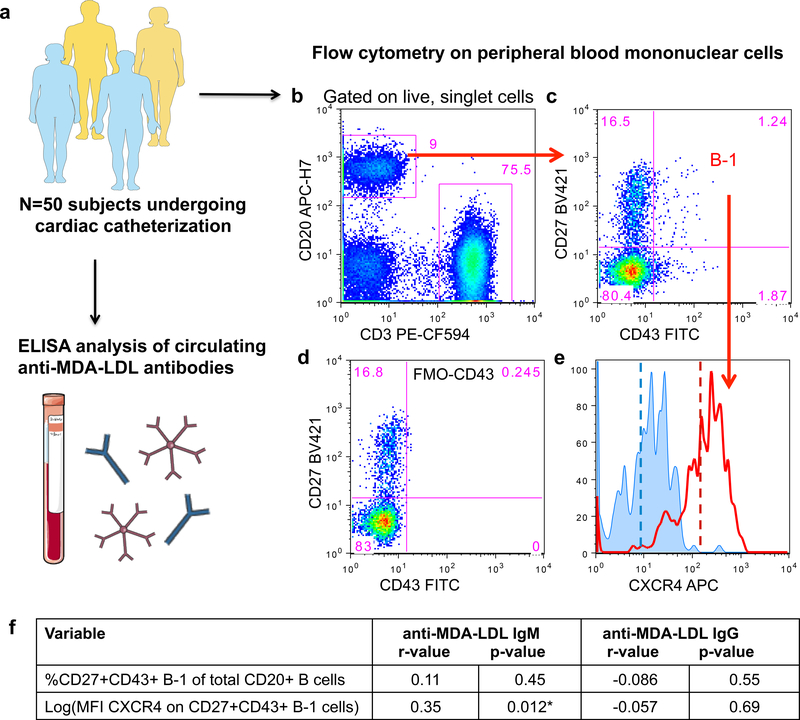
Figure 6. CXCR4 expression on peripheral human B-1 cells associates with increased circulating amounts of anti-MDA-LDL IgM antibodies.
(a), A 50-subject human cohort was analyzed for circulating anti-MDA-LDL IgM or IgG antibody levels and CXCR4 expression on peripheral blood B cell subsets. (b) Representative flow cytometry of peripheral blood mononuclear cells subset into CD20+ B cells and CD3+ T cells. (c) CD20+ B cells further subset into CD27+CD43+ B-1 cells. (d) FMO minus CD43 control used to set CD43 positivity. (e) Representative histograms depicting CXCR4 expression on the CD27+CD43+ B-1 subset from an FMO minus CXCR4 control (blue histogram) or a representative patient sample (red histogram). Dashed lines indicate mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CXCR4. (f) The percentage of CD20+CD3−CD27+CD43+ B-1 cells of total CD20+ B cells, or CXCR4 expression on B-1 cells (log(MFI CXCR4)) correlated with circulating amounts of anti-MDA-LDL IgM or IgG antibodies in 50 subjects. Correlation data presented as correlation coefficient (r) and statistical significance (p).