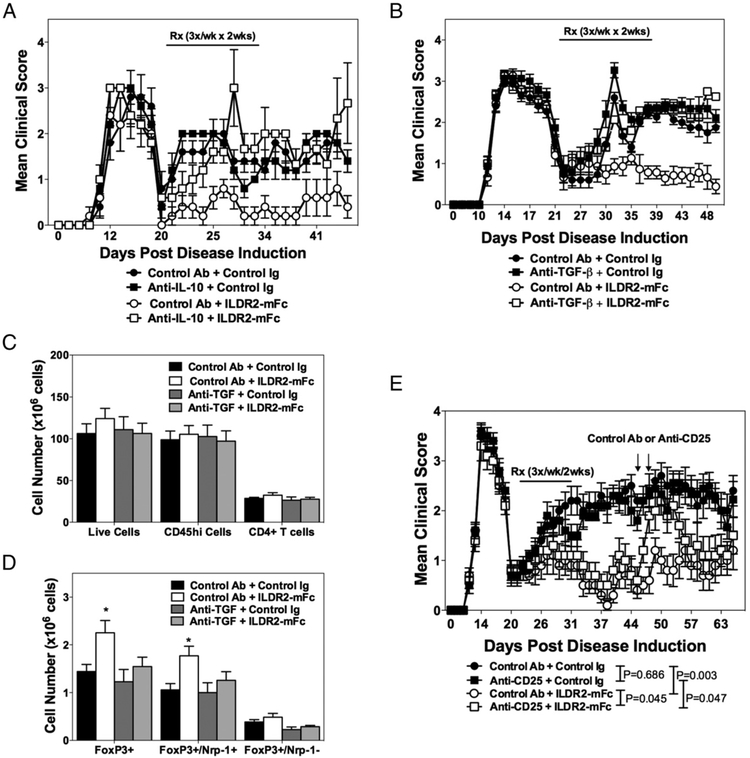
FIGURE 4.
Abolishment of ILDR2-mFc-mediated tolerance by Treg blockade with anti-IL-10 or anti–TGF-β, and transient Treg neutralization with anti-CD25 Abs. SJL/J mice were primed with PLP139–151/CFA. Starting from disease remission, mice were treated with ILDR2-mFc or control Ig (mIgG2a). These treatments were followed by a second injection of anti–IL-10 or control Ab (rat IgG1) (days 20–31; n = 5, experiment completed once) (A) or anti–TGF-β or control Ab (mouse IgG1) (B) (days 20–31; n = 15, experiment completed twice). All treatments were given i.p. at 100 μg per dose, three times a week for 2 wk. In the latter study, splenocytes were analyzed on day 44 for the presence of total live cells, CD45hi immune cells, and total CD4+ T cells (C), and the cell number for different Foxp3+ Treg subsets was determined (D). A few mice died in these studies as a result of disease exacerbation and were not scored further: two mice died on day 28 in the anti–IL-10 + ILDR2-mFc treatment group in the study presented in (A). In the study presented in (B), one mouse died on day 31 in the anti–TGF-β + control Ig group, and one died on day 36 in the control Ab + ILDR2-mFc group; in the anti–TGF-β + ILDR2-mFc treatment group, one mouse died on day 35, and another died on day 36. (E) In another study, transient Treg neutralization was induced 2 wk after the last ILDR2-mFc or control Ig (mIgG2a) administration by two injections of anti-CD25 or control Ab (rat IgM), at 500 μg per dose, on days 46 and 48 (indicated by arrows). Statistical analysis of anti-CD25 effect was carried out starting from the day of anti-CD25 or control Ab administration until day 58, because of the transient effect of the anti-CD25 Ab. One representative experiment of two is presented. *p < 0.05 versus control Ig.