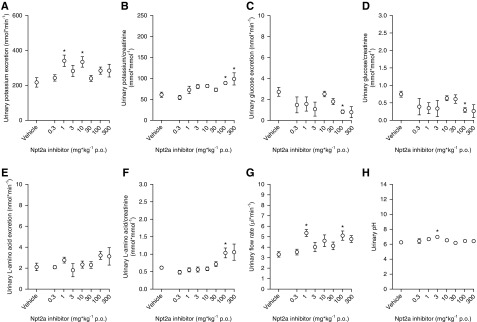
Figure 2.
Short-term Npt2a inhibition does not result in a clear dose-dependent effect on urinary potassium, glucose, or L-amino acid excretion, urinary flow rate, or urinary pH. Response to acute oral (p.o.) application of Npt2a-I (0.3–300 mg/kg via oral gavage) or vehicle in short-term (3 hour) metabolic cage experiments. (A) A clear dose-dependent increase in urinary potassium excretion in absolute terms, and (B) when corrected by urinary creatinine, was absent. Similar results were obtained for urinary glucose (C) and L-amino acid excretion (E) in absolute terms and when corrected by urinary creatinine (D and F, respectively). There was also no effect on urinary flow rate (G) or urinary pH (H). Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett multiple comparisons test and are expressed as mean±SEM. n=6–14 for 0.3–100 mg/kg; n=3 for 300 mg/kg. *P<0.05 versus vehicle.