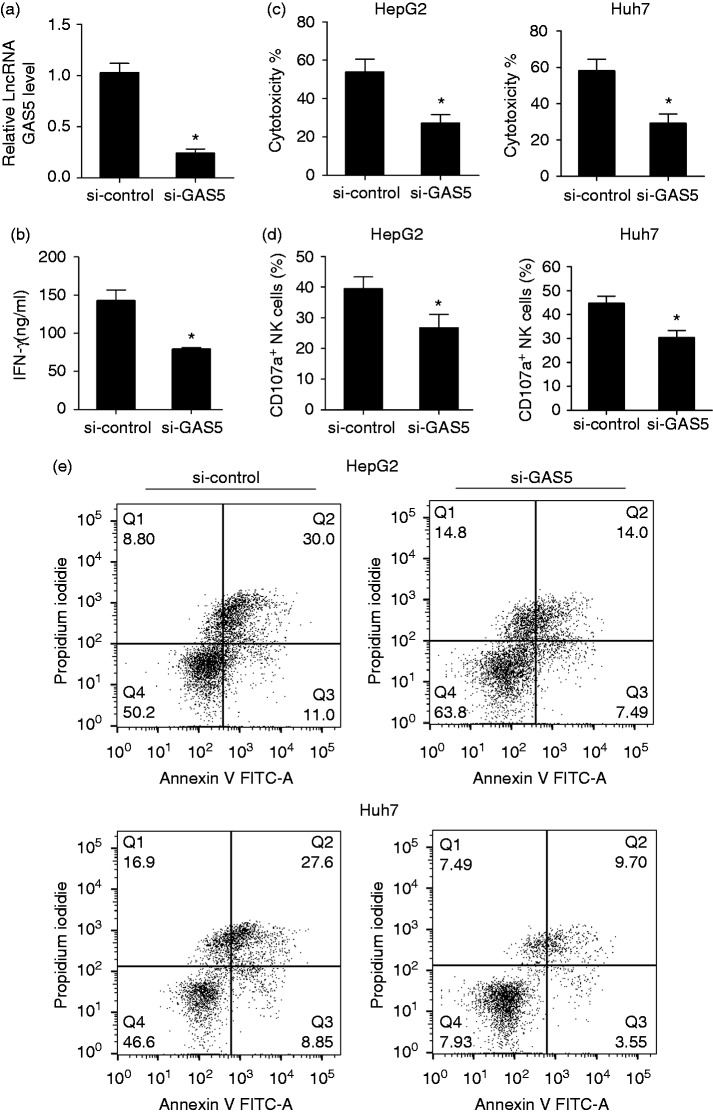
Figure 3.
lncRNA GAS5 knockdown inhibited the killing effect of NK cells. NK92 cells were activated by IL-2 (100 U/ml) and transfected with si-control or si-GAS5. (a) lncRNA GAS5 was down-regulated in the si-GAS5 group compared with the si-control group. (b) IFN-γ secretion in the supernatant was decreased in the si-GAS5 group compared with the si-control group. (c) After transfection with si-control or si-GAS5, NK cells were co-cultured with HepG2 cells, and cytotoxicity was detected by the CytoTox 96 non-radioactive cytotoxicity assay. Cytotoxicity was decreased in the si-GAS5 group compared with the si-control group. After co-culturing NK92 cells and Huh7 cells, cytotoxicity was decreased in the si-GAS5 group compared with the si-control group. (d) Lysosome marker CD107a of NK cells was detected by flow cytometry. The percentage of CD107a+ of NK cells was decreased in the si-GAS5 group compared with the si-control group. (e) Annexin V-PI double staining assay was used to detect the apoptosis of HepG2 and Huh7 cells. HepG2 cells were divided into si-control and si-GAS5 groups, and the apoptosis rate in si-GAS5 group was reduced compared with si-control group (41% vs 21.49%). Huh7 cells were divided into si-control and si-GAS5 groups, and the apoptosis rate in si-GAS5 group was reduced compared with si-control group (36.45% vs 13.25%). *P < 0.05, compared with si-control.