Figure 1.
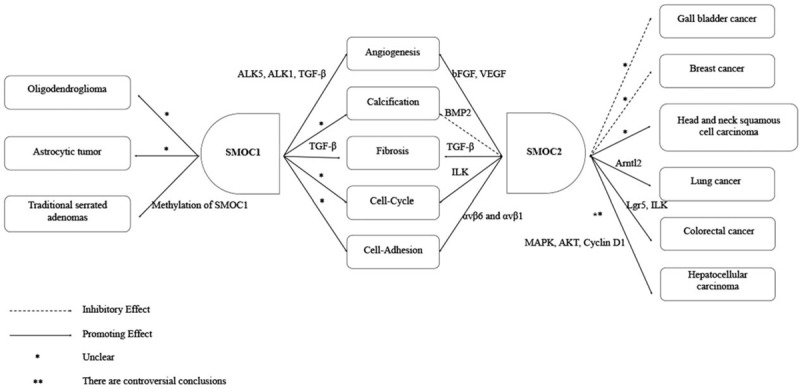
Illustration of basic SMOC functions in cells. Both SMOC1 and SMOC2 proteins are differentially expressed in various cells and tissues, which also function differently for embryonic development, homeostasis, and disease processes, that is, both SMOC1 and SMOC2 can promote angiogenesis, fibrosis, cell cycle progression, and cell adhesion. Molecularly, SMOC1 was able to regulate ALK5, ALK1, TGF-β, whereas SMOC2 regulated bFGF, VEGF in the angiogenesis process, although both SMOC1 and SMOC2 could regulate TGF-β in tissue fibrosis. SMOC2 can also regulate ILK in cell-cycle progression and αvβ6 and αvβ1 in the cell adhesion process, whereas the molecular mechanisms of SMOC1 in these two processes are not currently clear. SMOC1 enhanced calcification, but the underlying molecular mechanism remains to be defined. SMOC2 was able to inhibit calcification via the BMP2 signaling. Furthermore, SMOC1 deteriorated progression of oligodendrogliomas, astrocytic tumors, and traditional serrated adenoma, while SMOC2 is a risk factor for the development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. SMOC2 can also act as a tumor suppressor in gallbladder and breast cancers. The potential mechanism involved in traditional serrated adenoma development was due to SMOC1 methylation, but the molecular mechanisms of SMOC1 involved in oligodendroglioma and astrocytic tumor are unclear. SMOC2 might regulate Arntl2 in lung cancer, Lgr5, and ILK in colorectal cancer development and interact with MAPK, AKT, and Cyclin D1 in HCC, but the role of SMOC2 in HCC development remains controversial. The potential mechanisms of SMOC2 involved in gallbladder and breast cancers as well as head and neck squamous cell carcinoma remains unknown. ALK: Activin-like kinase; Akt: protein kinase B; Arntl2: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like 2; bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; ILK: Integrin-linked kinase; Lgr5: Leucine-rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; SMOC: Secreted modular calcium-binding protein; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor- β; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
