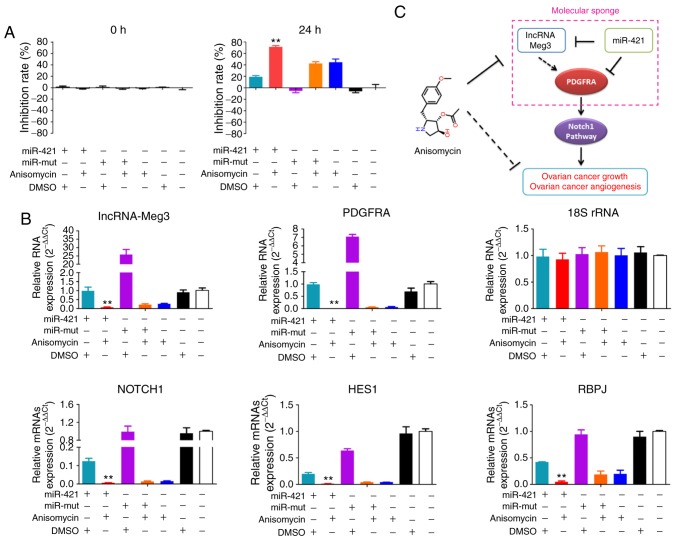
Figure 10.
miR-421 enhances the inhibitory effect of anisomycin on HuOCSCs. (A) MTT results showed that overexpression of miR-421 and treatment with anisomycin resulted in more severe proliferation inhibition of HuOCSCs, than either treatment alone. **P<0.01 vs. DMSO group (n=4). (B) Quantitative PCR results showed that overexpression of miR-421 and treatment with anisomycin decreased the expression of lncRNA-Meg3, PDGFRA, Notch1, HES1 and RBPJ. **P<0.01 vs. DMSO group (n=4). (C) Schematic of the proposed molecular mechanism of anisomycin inhibition of the activity and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer cells, by attenuating the molecular sponge effect in the lncRNA-Meg3/miR-421/PDGFRA axis. miR, microRNA; HuOCSCs, human ovarian cancer stem cells; lncRNA, long non-coding RNA; Meg3, maternally expressed 3; PDGFRA, platelet derived growth factor receptor α; HES1, hes family bHLH transcription factor 1; RBPJ, recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin κ J region; mut, mutant.