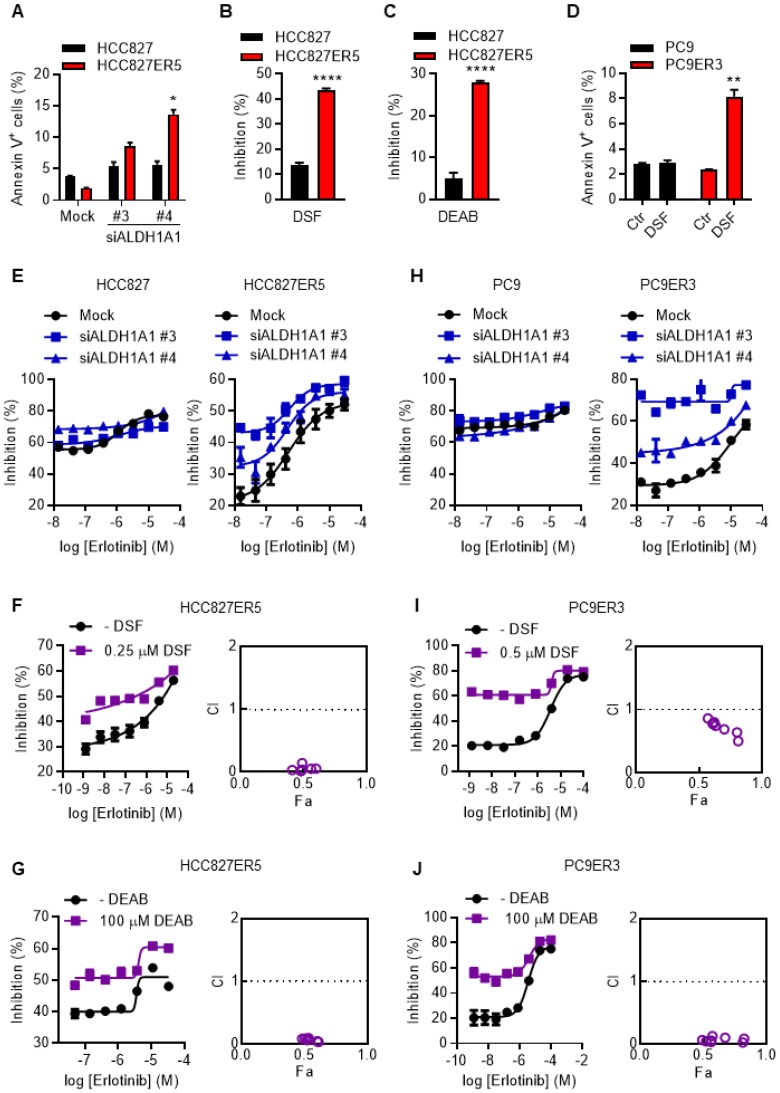
Figure 1.
ALDH1A1 dependence in erlotinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells. (A) ALDH1+ erlotinib-resistant HCC827-ER5 cells were more sensitive to ALDH1A1 knockdown than parental HCC827 cells. The cells were transfected with 30 nM ALDH1A1 siRNA or mock siRNA control for 72 h, stained with PI and FITC-labeled Annexin V, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Annexin V-positive cells indicated the cell undergoing apoptosis. (B-C) HCC827-ER5 cells showed more sensitivity to ALDH1 inhibition analyzed using the CCK8 cell viability assay. The cells were exposed to ALDH1 inhibitors, 1 μM DSF (B) or 100 μM DEAB (C) for 72 h. DSF, disulfiram; DEAB, N,N-diethylaminobenzaldehyde. (D) The ALDH1+ erlotinib-resistant PC9-ER3 cells showed more sensitivity to ALDH1 inhibition. The cells were exposed to 1 μM DSF for 24 h. (E and H) Knockdown of ALDH1A1 selectively enhanced the cell viability inhibition effect of erlotinib on HCC827-ER5 (E, right panel) and PC9-ER3 (H, right panel) cells, but not their parental counterparts (E and H, left panels). The cells were exposed to siRNA (30 nM) with erlotinib for 72 h. (F-G) Synergistic effect of ALDH1 inhibition by DSF (F) or DEAB (G) with erlotinib treatment on HCC827-ER5. (I-J) Synergistic effect on PC9-ER3 cells. The cells were co-treated with erlotinib and DSF or DEAB for 72 h. CI value (combination index) was calculated as described in the Materials and methods; CI = 0.85-0.9, slight synergism; CI = 0.7-0.85, moderate synergism; CI = 0.3-0.7, synergism; CI = 0.1-0.3, strong synergism; CI < 0.1, very strong synergism. Data represent the mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. In cases where error bars are not apparent, they lie within the space occupied by the symbol.