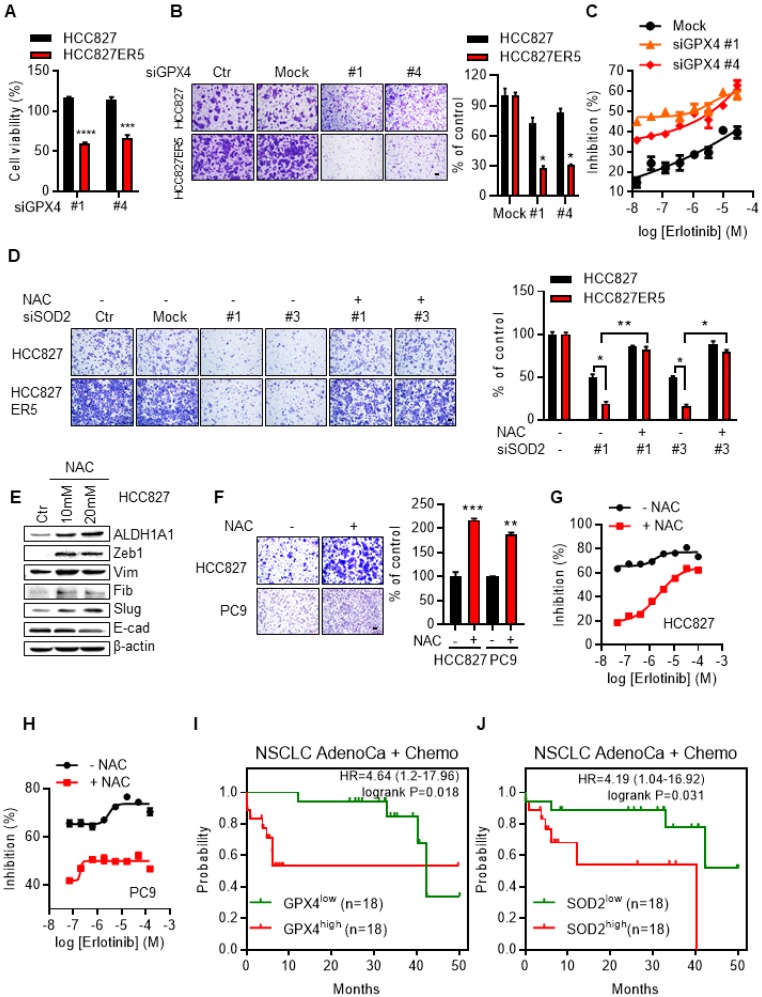
Figure 5.
ALDH1A1-addicted erlotinib-resistant cells depend on ROS-RCS metabolic pathway. (A-B) Knockdown of RCS mitigating enzyme GPX4 selectively inhibited HCC827-ER5 cell viability (A) and migration (B). The cells were transfected with siRNA for 72 h. (C) GPX4 knockdown re-sensitized HCC827-ER5 cells to erlotinib-induced inhibition of cell viability. The cells were transfected with siRNA for 72 h. (D) Knockdown of SOD2 selectively abrogated the elevated migration in HCC827-ER5 cells, and the effect was reversed by ROS and RCS scavenger N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC). The cells were transfected with SOD2 or mock control siRNA for 72 h. NAC (10 mM) was added 6 h before the point of the migration measurement. (E-F) Scavenging of ROS-RCS induced EMT properties assayed by mesenchymal/epithelial marker analysis (E) and migration ability analysis (F). The cells were exposed to 10 or 20 mM (E) or 10 mM (F) NAC for 6 h. (G-H) Scavenging ROS-RCS rendered HCC827 and PC9 parental cells less sensitive to erlotinib. The cells were exposed to 10 mM NAC for 6 h. (I-J) Kaplan-Meier analysis of the association between the probability of overall survival (OS) of lung adenocarcinoma patients who were received chemotherapy (n=36) and their GPX4 (I) and SOD2 (J) gene expression profiles. The analysis was performed by using the online KM-plotter tool (http://kmplot.com/analysis/index.php?p=service&cancer=lung) basing on the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases GSE29013 and GSE14814. Low or high levels of gene were defined as higher or lower than the median value of 36 patients. Ctr, solvent control; NSCLC, non-small-cell lung carcinoma; AdenoCa, adenocarcinoma; Chemo, with chemotherapy.