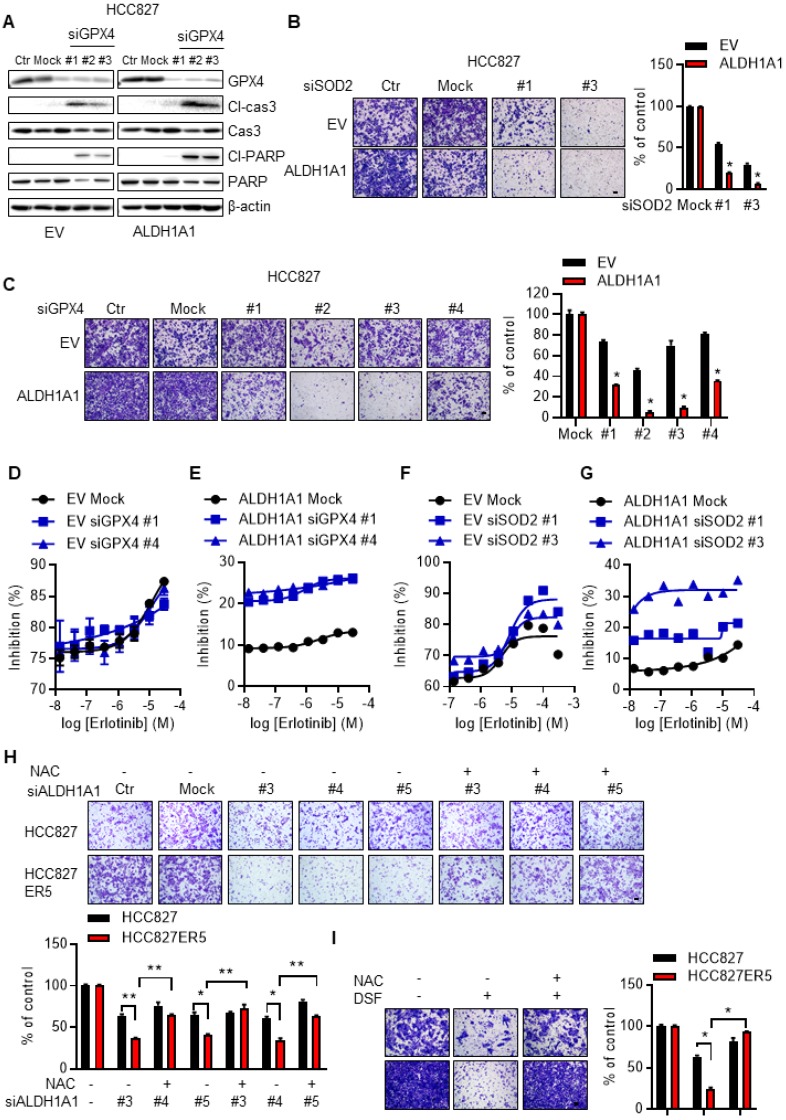
Figure 6.
ALDH1A1-conferred resistance to erlotinib depends on the ROS/RCS metabolic pathway. (A) Knockdown of GPX4 induced apoptosis more in HCC827-ALDH1A1 than in the control cells, assayed by western blot analysis of the apoptotic markers, cleaved caspase 3 (Cl-cas3) and cleaved PARP (Cl-PARP). The cells were transfected with 20 nM GPX4 siRNA for 72 h. (B-C) Knockdown of SOD2 (B) or GPX4 (C) abrogated the ALDH1A1-induced effect on the enhancement of cell migration ability. The cells were transfected with 20 nM GPX4 or SOD2 siRNA for 72 h. Mock data of each corresponding cell line as control. (D-G) Knockdown of GPX4 (D and E) or SOD2 (F and G) sensitized the effect of erlotinib-induced cell viability inhibition more in HCC827-ALDH1A1 (E and G) than in the control (D and F) cells. The cells were transfected with 20 nM GPX4 or SOD2 siRNA for 72 h. (H-I) Suppression of ALDH1A1 by siRNA (H) or inhibitor (I) abrogated the enhanced migration ability of HCC827-ER5 cells, and the ALDH1A1-mediated effect was reversed by NAC. The cells were transfected with ALDH1A1 or mock control siRNA for 72 h, or exposed to 100 μM DSF for 6 h with or without 10 mM NAC for 6 h, and the migration ability was measured in fresh media without the above-mentioned reagents. Mock (H) or DSF/NAC free (I) data of each corresponding cell line as control.