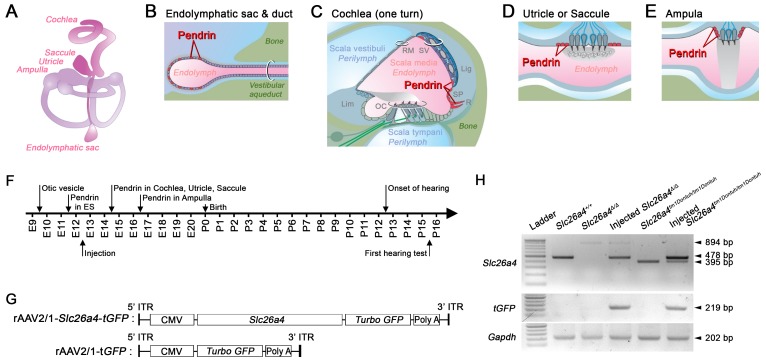
Figure 1.
Transcription of recombinant viral vectors in the embryonic inner ear. (A) Schematic diagram of the membranous inner ear. (B-E) Schematic diagrams of parts of the inner ear where natural pendrin expression occurs. (B) Schematic cross-section of the endolymphatic sac and duct. (C) Schematic cross-section of one turn of the cochlea. Lig, spiral ligament; Lim, limbus; OC, organ of Corti; RM, Reissner's membrane; R, root cell; SP, spiral prominence; SV, stria vascularis. (D) Schematic cross-section of the utricle or saccule. (E) Schematic cross-section of an ampulla. (F) Onset of pendrin expression in different parts of the inner ear during development from embryonic (E) day 9 to postnatal (P) day 16. (G) Schematic diagrams of viral vectors. The rAAV2/1-Slc26a4-tGFP vector expressed Slc26a4 and turbo GFP (tGFP) driven by the same CMV promoter. The rAAV2/1-tGFP vector, which was used as a control, expressed only tGFP under the control of the CMV promoter. CMV, cytomegalovirus; ITR, inverted terminal repeat from AAV2; Slc26a4, solute carrier family 26 member 4. GFP, green fluorescent protein. (H) mRNA expression in the inner ear. Transcripts of endogenous or vector-induced Slc26a4+ mRNA (478 bp), of Slc26a4Δ (894 bp) and Slc26a4tm1Dontuh (395 bp) mRNA as well as vector-induced tGFP (219 bp) mRNA and endogenous Gapdh (202 bp) mRNA were amplified by RT-PCR and separated by gel-electrophoresis. Reactions were performed with total RNA isolated from inner ears of Slc26a4+/+, Slc26a4Δ/Δ, rAAV2/1-Slc26a4-tGFP injected Slc26a4Δ/Δ, Slc26a4tm1Dontuh/tm1Dontuh, and rAAV2/1-Slc26a4-tGFP injected Slc26a4tm1Dontuh/tm1Dontuh mice. The ladder consisted of markers between 100 and 1000 bp in 100 bp intervals.